Japanese Yen trims a part of intraday gains against USD; USD/JPY rebounds from sub-140.00 levels
- The Japanese Yen continues to attract safe-haven flows amid persistent trade-related uncertainties.
- BoJ rate hike bets also lend support to the JPY and weigh on the USD/JPY pair amid a bearish USD.
- Trump's threat to the Fed’s independence keeps the USD on the defensive near a multi-year trough.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) retreats after touching a fresh multi-month high against its American counterpart earlier this Tuesday, with the USD/JPY pair rebounding over 40 pips from levels below the 140.00 psychological mark. However, any meaningful JPY depreciation still seems elusive as persistent trade-related uncertainties and geopolitical tensions might continue to underpin traditional safe-haven assets.
Furthermore, the growing acceptance that the Bank of Japan (BoJ) will raise interest rates again in 2025 could act as a tailwind for the JPY. The US Dollar (USD), on the other hand, languishes near a multi-year low amid the weakening confidence in the US economy and doubts about the Federal Reserve's (Fed) independence. This, along with the divergent BoJ-Fed expectations, should support the lower-yielding JPY.
Japanese Yen bulls retain control amid US tariff woes, hawkish BoJ expectations
- Following the first Japan-US negotiations last week, Japan's Economic Revitalization Minister Ryosei Akazawa said that any agreement would likely take some time as it's difficult to say how long it will take to bridge the gap between the two sides.
- Akazawa added that agriculture will not be compromised to protect the auto industry in US tariff talks. Meanwhile, Japan's Finance Minister Katsunobu Kato will meet US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent later this week to discuss currency rates.
- In its quarterly review of regional economic conditions across the country, the Japanese government maintained its overall economic assessment, warning of increasing downside risks due to US trade policies, per Xinhua News Agency.
- Investors remained on edge amid the uncertainty over US President Donald Trump’s steep tariffs and the effect of the erratic trade war on the global economy. Moreover, Trump’s fresh attack on Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell rattled markets.
- Trump accused Powell of not moving fast enough to bring down interest rates. Powell last week said that the central bank was not inclined to cut interest rates in the near future amid the possible inflationary pressures stemming from the new tariffs.
- Meanwhile, White House economic adviser Kevin Hassett has suggested that Trump and his team are studying if they could fire Powell. This raises doubts over the independence of the central bank and keeps the US Dollar bulls on the defensive.
- The Bank of Japan is reportedly planning to signal next week that there is almost no need to change its basic stance on raising interest rates as the potential impact of increased US tariffs will not disrupt the ongoing cycle of wage growth and inflation.
- This marks a big divergence in comparison to expectations that the Fed will resume its rate-cutting cycle in June and lower borrowing costs by one full percentage point by the end of this year. This should further benefit the lower-yielding JPY.
- Traders now look forward to the release of the Richmond Manufacturing Index from the US later this Tuesday. This, along with speeches from influential FOMC members, will drive the USD and provide short-term impetus to the USD/JPY pair.
- The focus will then shift to the global flash PMIs on Wednesday, which would offer a fresh insight into the global economic health. Apart from this, trade-related developments will play a key role in driving the market sentiment and the JPY demand.
USD/JPY shows some resilience below the 140.00 mark; not out of the woods yet
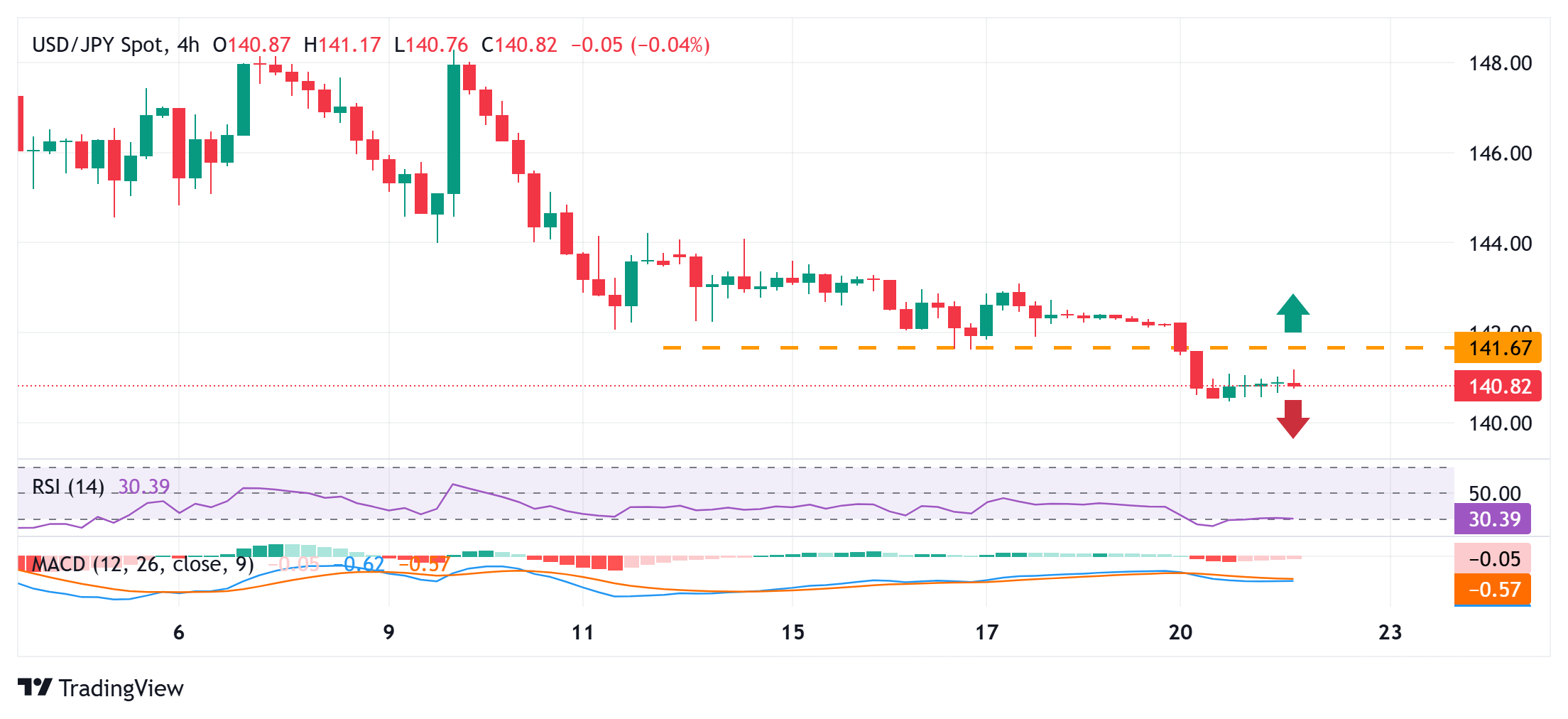
From a technical perspective, the slightly oversold daily Relative Strength Index (RSI) is holding back traders from placing fresh bearish bets around the USD/JPY pair. Any subsequent move up, however, is likely to confront stiff resistance near the 141.65-141.60 horizontal support breakpoint. That said, a sustained strength above could trigger a short-covering rally and lift spot prices beyond the 142.00 round figure, toward the next relevant hurdle near the 142.35-142.40 region.
On the flip side, the 140.45 area, or the multi-month low touched on Monday, now seems to protect the immediate downside, below which the USD/JPY pair could accelerate the fall toward the 140.00 psychological mark. The downward trajectory could extend further towards challenging the 2024 yearly swing low, around the 139.60-139.55 region.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.
