Gold price sticks to modest intraday gains, remains close to record high ahead of US NFP
- Gold price regains positive traction following the overnight modest pullback.
- Trade war fears continue to act as a tailwind for the safe-haven XAU/USD pair.
- Fed rate cut bets and subdued USD demand further lend support to the bullion.
Gold price (XAU/USD) sticks to its modest intraday gains through the first half of the European session on Friday and remains close to the all-time peak touched earlier this week. Concerns about the escalating US-China trade war and the potential economic fallout from US President Donald Trump’s aggressive trade policies continue to underpin demand for the safe-haven bullion.
Meanwhile, the US Dollar (USD) struggles to gain any meaningful traction amid bets that the Federal Reserve (Fed) would lower borrowing costs twice this year, which triggered the recent sharp decline in the US Treasury bond yields. This turns out to be another factor acting as a tailwind for the non-yielding yellow metal ahead of the crucial US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report.
Gold price is underpinned by a combination of supporting factors
- China announced tariffs on some US goods in retaliation to US President Donald Trump's 10% levy on Chinese imports. This marks a new trade war between the world's top two economies and continues to underpin the safe-haven Gold price.
- On the economic data front, the US Department of Labor (DoL) reported on Thursday that the number of US citizens filing new applications for unemployment insurance rose to 219K for the week ending February 1, from the previous week's revised tally of 208K.
- US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said on Thursday that the Trump administration was not particularly concerned about the Federal Reserve's trajectory on interest rates and that the focus is on bringing down 10-year Treasury yields.
- The yield on the benchmark 10-year US government bond fell to its lowest level since December 12 earlier this week amid bets that the Federal Reserve will cut rates twice by the end of 2025, further benefitting the non-yielding yellow metal.
- Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee noted that the appearance that inflation has stalled is largely due to base effects and that the central bank needs to be mindful of overheating and deterioration, but things are largely going well.
- Dallas Fed President Lorie Logan said that inflation progress has been significant, but the US labor market remains far too firm to push the central bank into rate cuts any time soon. This, however, does little to impress the US Dollar bulls.
- Market participants now look forward to the US Nonfarm Payrolls report, which is expected to show that the economy added 170K jobs in January compared to 256K in the previous month and the Unemployment rate held steady at 4.1%.
- The crucial data will influence market expectations about the Fed's interest rate outlook, which, in turn, should play a key role in driving the USD demand in the near term and determining the next leg of a directional move for the XAU/USD.
Gold price bulls seem reluctant amid slightly overbought conditions
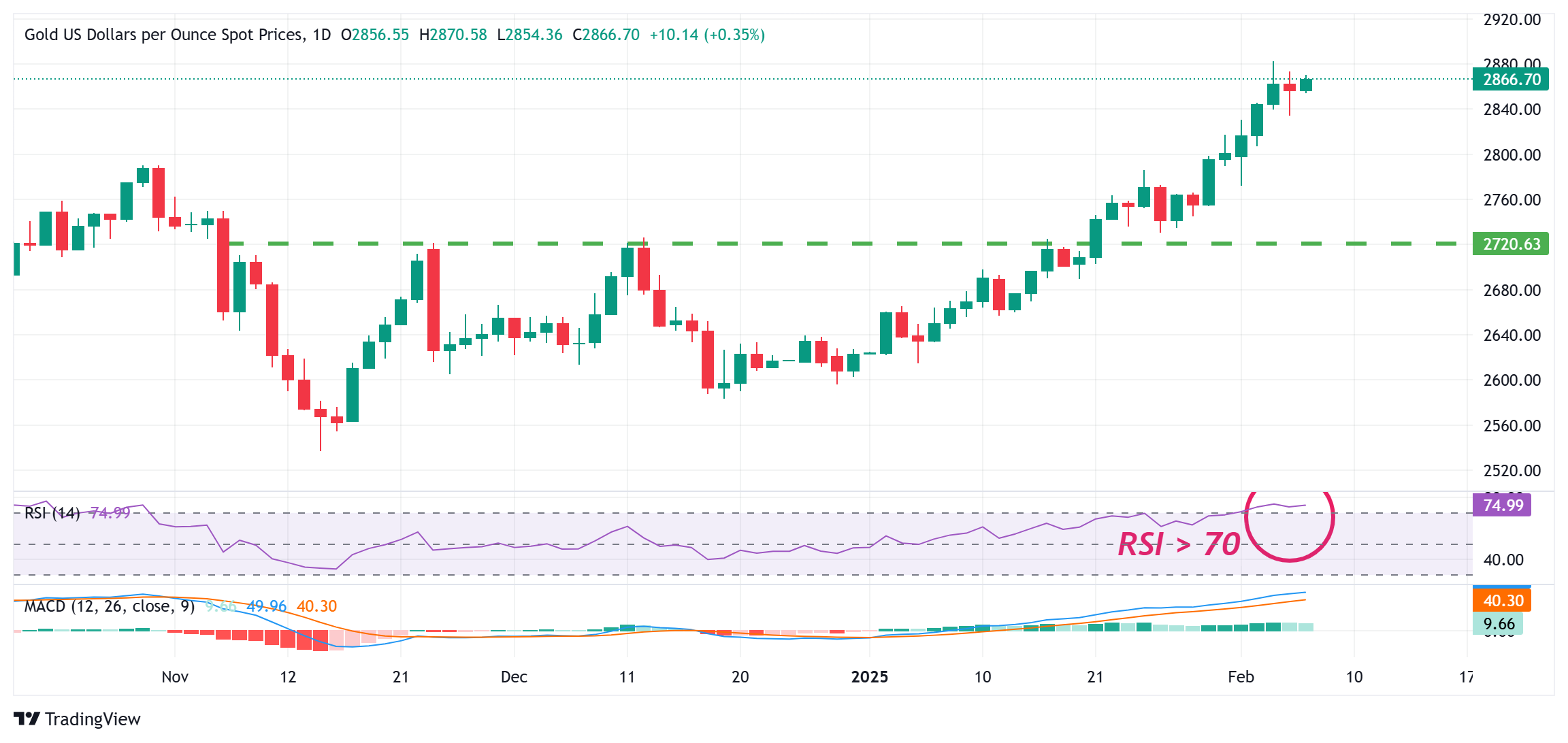
From a technical perspective, the overnight bounce and the subsequent move up on Friday validates the near-term positive outlook for the Gold price. That said, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) is flashing slightly overbought conditions on the day chart and warrants some caution for bullish traders. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for some near-term consolidation before positioning for an extension of the recent well-established uptrend from the December monthly trough.
In the meantime, the $2,855 horizontal zone, followed by the overnight swing low, around the $2,834 region, could offer some support to the Gold price ahead of the $2,815-2,714 region. This is followed by the $2,800 mark, which if broken decisively might prompt some technical selling and drag the XAU/USD towards the $2,773-2,772 resistance breakpoint. The latter coincides with the weekly low and a convincing break below should pave the way for a deeper corrective decline.
Economic Indicator
Nonfarm Payrolls
The Nonfarm Payrolls release presents the number of new jobs created in the US during the previous month in all non-agricultural businesses; it is released by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The monthly changes in payrolls can be extremely volatile. The number is also subject to strong reviews, which can also trigger volatility in the Forex board. Generally speaking, a high reading is seen as bullish for the US Dollar (USD), while a low reading is seen as bearish, although previous months' reviews and the Unemployment Rate are as relevant as the headline figure. The market's reaction, therefore, depends on how the market assesses all the data contained in the BLS report as a whole.
Read more.Next release: Fri Feb 07, 2025 13:30
Frequency: Monthly
Consensus: 170K
Previous: 256K
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
America’s monthly jobs report is considered the most important economic indicator for forex traders. Released on the first Friday following the reported month, the change in the number of positions is closely correlated with the overall performance of the economy and is monitored by policymakers. Full employment is one of the Federal Reserve’s mandates and it considers developments in the labor market when setting its policies, thus impacting currencies. Despite several leading indicators shaping estimates, Nonfarm Payrolls tend to surprise markets and trigger substantial volatility. Actual figures beating the consensus tend to be USD bullish.
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.