US Dollar goes nowhere with traders already looking forward to next week's data
- The US Dollar further consolidates on Friday after weakening further on Thursday.
- Traders have devalued the US Dollar a touch, amidst the Bank of Japan and Bank of England’s decisions to keep rates on hold.
- The US Dollar Index falls outside its tight bandwidth, a sign that could dive lower next week.
The US Dollar (USD) trades broadly steady on Friday after Thursday’s sharp decline, when traders revalued the Greenback after the US Federal Reserve (Fed) joined the European Central Bank (ECB) and several others by starting its interest-rate cutting cycle. Quite a different picture comes from the Bank of England (BoE) and the Bank of Japan (BoJ), which decided to keep interest rates steady, causing the US Dollar to struggle against the British Pound (GBP) and the Japanese Yen (JPY).
On the economic data front, the US economic calendar is quite empty, which is ideal for traders to let the dust settle after a volatile week. Next week, a lot of US data is set to be released. The main elements include the final US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data for Q2 and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, the Fed’s preferred inflation gauge.
Daily digest market movers: All is quiet
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ) has kept its interest rate stable at 0.25%. BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda mentioned that inflation came in a little softer than anticipated, that the BoJ is keeping a close eye on the economic data, and that it is ready to hike at any moment when needed.
- Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia President Patrick Harker delivers a speech titled "The Federal Reserve: it's more than just interest rates" at the Tulane University Freeman School of Business Lecture in New Orleans at around 18:00 GMT.
- Equity markets are facing some profit taking after the steep rallies that took place in the aftermath of the Fed rate decision. European equities are slumping near 1% lower, while US futures are dragging by 0.5% ahead of the US opening bell.
- The CME Fedwatch Tool shows a 59.3% chance of a 25-basis-point rate cut at the next Fed meeting on November 7. The remaining 40.7% is pricing in another 50-basis-point rate cut.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 3.74%, rather in the higher end of this week’s range between 3.60% and 3.76%.
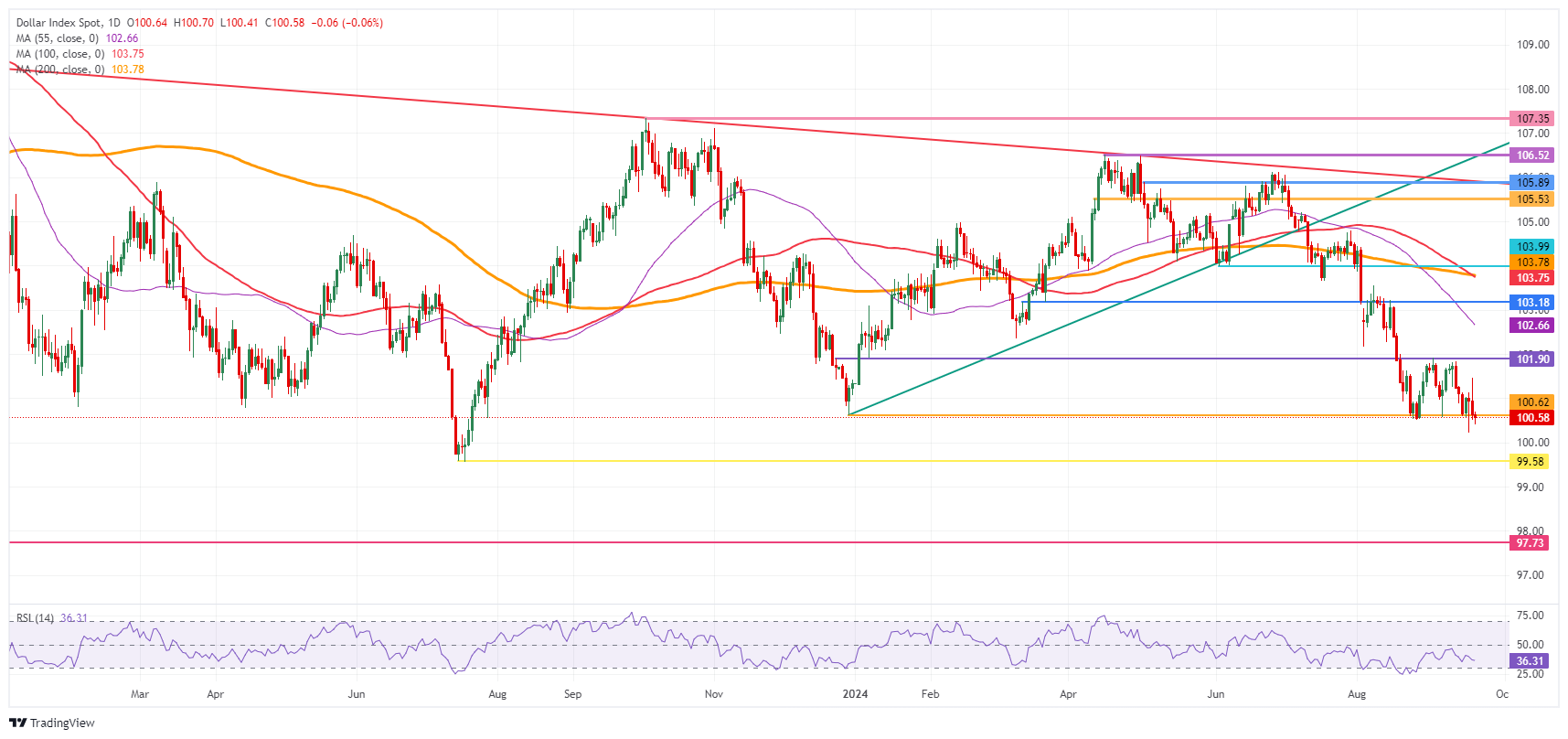
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Data driven week ahead
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is in a precarious situation. A weekly close below that line in the sand of 100.62 could point to further weakness ahead. A further depreciation could take place next week if US data eases further, opening the door to another big rate cut in November.
The upper level of the recent range remains 101.90, with the DXY still possible to recover above 100.62 first. Further up, the index could go to 103.18, with the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 102.66 on the way. The next tranche up is very misty, with the 200-day SMA and the 100-day SMA at 103.76, just ahead of the big 104.00 round level.
On the downside, 100.62 (the low from December 28, 2023) is being broken again and could point to more weakness ahead. Should that take place next week, the low from July 14, 2023, at 99.58, will be the next level to look out for. If that level gives way, early levels from 2023 are coming in near 97.73.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Interest rates FAQs
Interest rates are charged by financial institutions on loans to borrowers and are paid as interest to savers and depositors. They are influenced by base lending rates, which are set by central banks in response to changes in the economy. Central banks normally have a mandate to ensure price stability, which in most cases means targeting a core inflation rate of around 2%. If inflation falls below target the central bank may cut base lending rates, with a view to stimulating lending and boosting the economy. If inflation rises substantially above 2% it normally results in the central bank raising base lending rates in an attempt to lower inflation.
Higher interest rates generally help strengthen a country’s currency as they make it a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
Higher interest rates overall weigh on the price of Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold instead of investing in an interest-bearing asset or placing cash in the bank. If interest rates are high that usually pushes up the price of the US Dollar (USD), and since Gold is priced in Dollars, this has the effect of lowering the price of Gold.
The Fed funds rate is the overnight rate at which US banks lend to each other. It is the oft-quoted headline rate set by the Federal Reserve at its FOMC meetings. It is set as a range, for example 4.75%-5.00%, though the upper limit (in that case 5.00%) is the quoted figure. Market expectations for future Fed funds rate are tracked by the CME FedWatch tool, which shapes how many financial markets behave in anticipation of future Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.