Gold price stands firm near multi-month peak; seems poised to climb further
- Gold price scales higher for the third straight day amid the global flight to safety.
- Bets for more rate cuts by the Fed also benefit the non-yielding yellow metal.
- A modest USD bounce and the risk-on mood cap gains for the XAU/USD pair.
Gold price (XAU/USD) sticks to positive bias for the third successive day on Wednesday and trades near its highest level since November 1 during the first half of the European session. The uncertainty around US President Donald Trump's trade policies turns out to be a key factor that continues to drive haven flows towards the precious metal. Apart from this, expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut rates twice this year lend additional support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
That said, the upbeat market mood, along with rebounding US Treasury bond yields and a modest US Dollar (USD) recovery from a two-week low, acts as a headwind for the Gold price. Nevertheless, the fundamental backdrop seems tilted firmly in favor of bullish traders and supports prospects for an extension of the XAU/USD positive move witnessed over the past month or so. Hence, any meaningful corrective slide might still be seen as a buying opportunity and is likely to remain limited.
Gold price bulls have the upper hand amid trade war fears; modest uptick in US bond yields and USD cap gains
- Hours after taking the oath, US President Donald Trump said that he intends to impose 25% tariffs on Canada and Mexico, and the target date for tariffs would be as soon as early February.
- Trump's tariff remarks sparked concerns about a fresh wave of global trade war, boosting demand for safe-haven assets and lifting the Gold price to its highest level since early November.
- Signs of abating inflation in the US revived bets that the Federal Reserve may not exclude the possibility of rate cuts by the end of this year, which dragged the US Treasury bond yields lower.
- This, along with the Israel-Hamas ceasefire agreement, and hopes that Trump might relax curbs on Russia in exchange for a deal to end the Ukraine war, remain supportive of the risk-on mood.
- The US Dollar gains some positive traction during the Asian session on Wednesday and moves away from a two-week trough that was retested on Tuesday, which might cap gains for the XAU/USD.
- Investors now look forward to the highly-anticipated Bank of Japan decision on Friday, which could infuse volatility in the financial markets and influence the safe-haven precious metal.
- Apart from this, the flash PMI prints would offer a fresh insight into the global economic health and provide some meaningful impetus to the commodity during the latter half of the week.
Gold price seems poised to build on the overnight breakout momentum above the $2,720 strong resistane
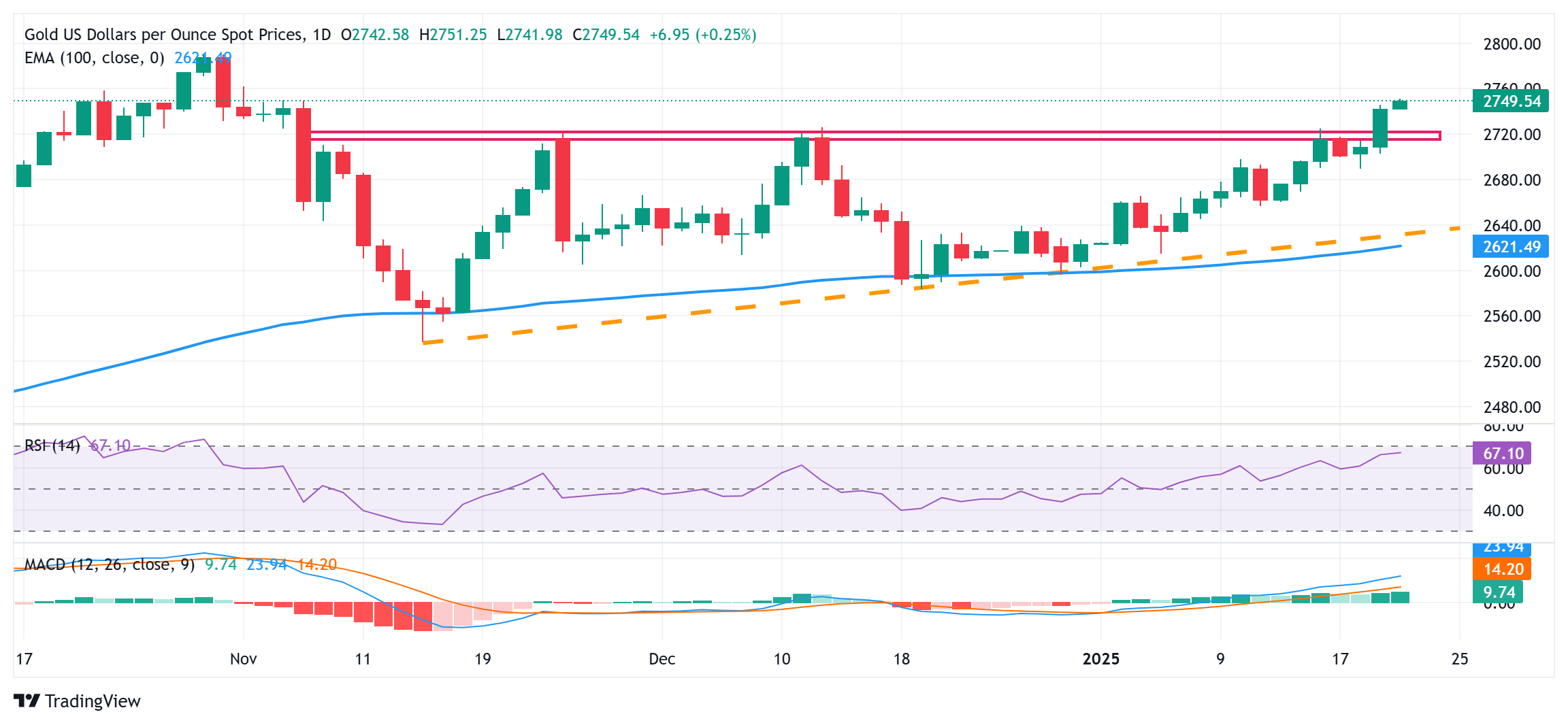
From a technical perspective, the overnight breakout through the $2,720 supply zone was seen as a fresh trigger for bullish traders. Given that oscillators on the daily chart are holding comfortably in positive territory and are still away from being in the overbought zone, a subsequent strength beyond the $2,748-2,750 hurdle should pave the way for additional gains. The Gold price might then aim towards challenging the all-time peak, around the $2,790 area touched in October 2024.
On the flip side, any corrective pullback might now be seen as a buying opportunity and remain limited near the $2,725-2,720 region. The next relevant support is pegged near the $2,700-2,690 area, which if broken decisively might prompt aggressive technical selling and drag the Gold price to the $2,660 zone en route to the $2,625 confluence. The latter comprises the 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and an ascending trend-line extending from the November swing low, which, in turn, should act as a key pivotal point and help determine the next leg of a directional move for the XAU/USD.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.
