USD/INR surges as Fed drags Indian Rupee to record low
- The Indian Rupee attracts some seller to an all-time low in Thursday’s Asian session.
- Persistent demand for USD and a cautious outlook from Fed officials might add further pressure on the INR.
- The US weekly Initial Jobless Claims, Existing Home Sales and final reading of Q3 GDP data will be released later on Thursday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) falls to near a fresh record low on Thursday. The renewed US Dollar (USD) demand from importers, foreign banks, foreign fund outflows and a muted trend in domestic equities further undermine the local currency. Furthermore, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) lowered its key interest rate by a quarter percentage point at its December meeting on Wednesday and also projected a slower pace of cuts in 2025. This, in turn, boosts the Greenback against the INR.
Nonetheless, the downside of the INR might be limited as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to intervene in the market to prevent excess volatility. Traders will keep an eye on the US weekly Initial Jobless Claims, Existing Home Sales and final reading of Gross Domestic Product Annualized for the third quarter (Q3), which are due later on Thursday.
Indian Rupee remains weak after the Fed hawkish rate cut
- A rise in gold imports that widened India's trade deficit to a record in November and pushed the INR to a record low was due to an error in calculation, Bloomberg News reported on Wednesday, citing people with knowledge of the matter.
- “There is pressure on the rupee due to the demand for dollars from foreign clients. However, the rupee is performing better than other currencies. The depreciation is gradual. Now it is expected to trade in a narrow range and 85 per dollar level will be protected,” said the treasury head at a state-owned bank.
- On Wednesday, the Fed reduced the Federal Funds Rate by 25 basis points (bps) to a target range of 4.25%-4.50%, back to the level where it was in December 2022.
- The Fed expects to continue cutting rates next year, although it is now penciling in two rate cuts, down from the four it had forecast in September, according to the Summary of Economic Projections, or “dot plot”.
- The dot plot saw the committee lower its expected unemployment rate this year to 4.2% and raise its projection for 2024 Gross Domestic Product growth to 2.5%.
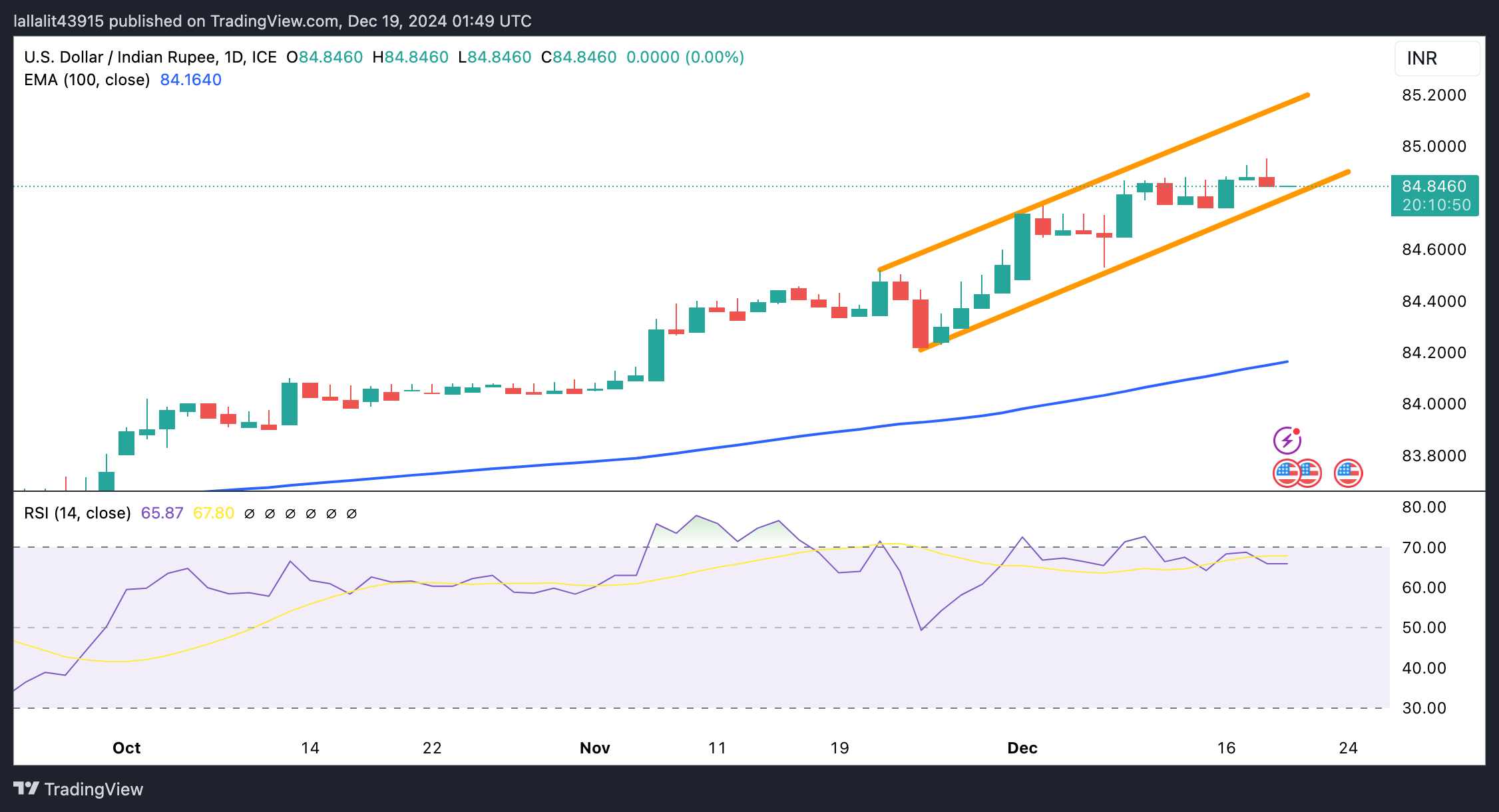
USD/INR’s broader trend remains constructive
The Indian Rupee trades on a weaker note on the day. The USD/INR pair maintains a strong uptrend on the daily chart, with the price holding above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The path of least resistance is to the upside as the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is above the midline near 65.85, suggesting bullish pressure is present.
The ascending trend channel and the psychological level of 85.00 appear to be a tough nut to crack for bulls. The breakout above this level could see a rally to the next upside target at 85.50.
On the other hand, the initial support level emerges at 84.82, the lower boundary of the trend channel. A breach of the mentioned level could expose 84.22, the low of November 25. Bearish candlesticks could see a drop to 84.16, the 100-day EMA.
Indian economy FAQs
The Indian economy has averaged a growth rate of 6.13% between 2006 and 2023, which makes it one of the fastest growing in the world. India’s high growth has attracted a lot of foreign investment. This includes Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into physical projects and Foreign Indirect Investment (FII) by foreign funds into Indian financial markets. The greater the level of investment, the higher the demand for the Rupee (INR). Fluctuations in Dollar-demand from Indian importers also impact INR.
India has to import a great deal of its Oil and gasoline so the price of Oil can have a direct impact on the Rupee. Oil is mostly traded in US Dollars (USD) on international markets so if the price of Oil rises, aggregate demand for USD increases and Indian importers have to sell more Rupees to meet that demand, which is depreciative for the Rupee.
Inflation has a complex effect on the Rupee. Ultimately it indicates an increase in money supply which reduces the Rupee’s overall value. Yet if it rises above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 4% target, the RBI will raise interest rates to bring it down by reducing credit. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (the difference between interest rates and inflation) strengthen the Rupee. They make India a more profitable place for international investors to park their money. A fall in inflation can be supportive of the Rupee. At the same time lower interest rates can have a depreciatory effect on the Rupee.
India has run a trade deficit for most of its recent history, indicating its imports outweigh its exports. Since the majority of international trade takes place in US Dollars, there are times – due to seasonal demand or order glut – where the high volume of imports leads to significant US Dollar- demand. During these periods the Rupee can weaken as it is heavily sold to meet the demand for Dollars. When markets experience increased volatility, the demand for US Dollars can also shoot up with a similarly negative effect on the Rupee.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.