US Dollar set to close off week on the back foot after Michigan surprise reading
- The Greenback back in a weekly loss ahead of the US trading session on Friday.
- Headline risk persists with headlines on the government shutdown and tariff headwinds.
- The US Dollar Index has been limited by the 104.00 hurdle and looks to be closing off the week in a negative tone.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar (USD) against six major currencies, dips lower again on Friday after a few headlines on tariffs and the US spending bill. The index, which has been limited below the 104.00 hurdle this week, hasn’t moved that much despite rumors of a possible ceasefire deal by Ukraine, the first steps in the German spending plan voting and retaliations from Canada and Europe on US tariffs.
On the economic data front, the University of Michigan has published its preliminary consumer sentiment reading for March and the 5-year inflation expectation. Clearly sentiment is rotating with a substantial lower reading in consumer sentiment while inflation expectations are tilted to the upside.
Daily digest market movers: Consumer says NO
- Gold as a safe haven asset has breached the $3,000 mark this Friday in a recession-feared-induced rally where traders are much concerned about economic growth and the tariffs outlook, with reciprocal levies coming into effect in April.
- A government shutdown looks to be avoided after Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer is said to back the House-passed funding measure.
- The World Trade Organisation (WTO) has been requested by Canada to look into the possibility US President Donald Trump's tariffs are illegal, Bloomberg reports.
- The University of Michigan has released its preliminary reading for March:
- The US Consumer Sentiment Index fell to 57.9, a big deviation from the expected 63.1, coming from 64.7 in the final February reading.
- The US 5-year Consumer Inflation Expectation jumped to 3.9%, surging from 3.5% in the final February reading.
- Equities are making another attempt to brush off the negative tone for this week. All indices are up over 0.50% across Europe and in the US.
- The CME Fedwatch Tool projects a 97.0% chance for no interest rate changes in the upcoming Fed meeting on March 19. The chances of a rate cut at the May 7 meeting stand at 32.8% and 78.5% at June’s meeting.
- The US 10-year yield trades around 4.306%, off its near five-month low of 4.10% printed on March 4 and after hitting a five-day high on Thursday.
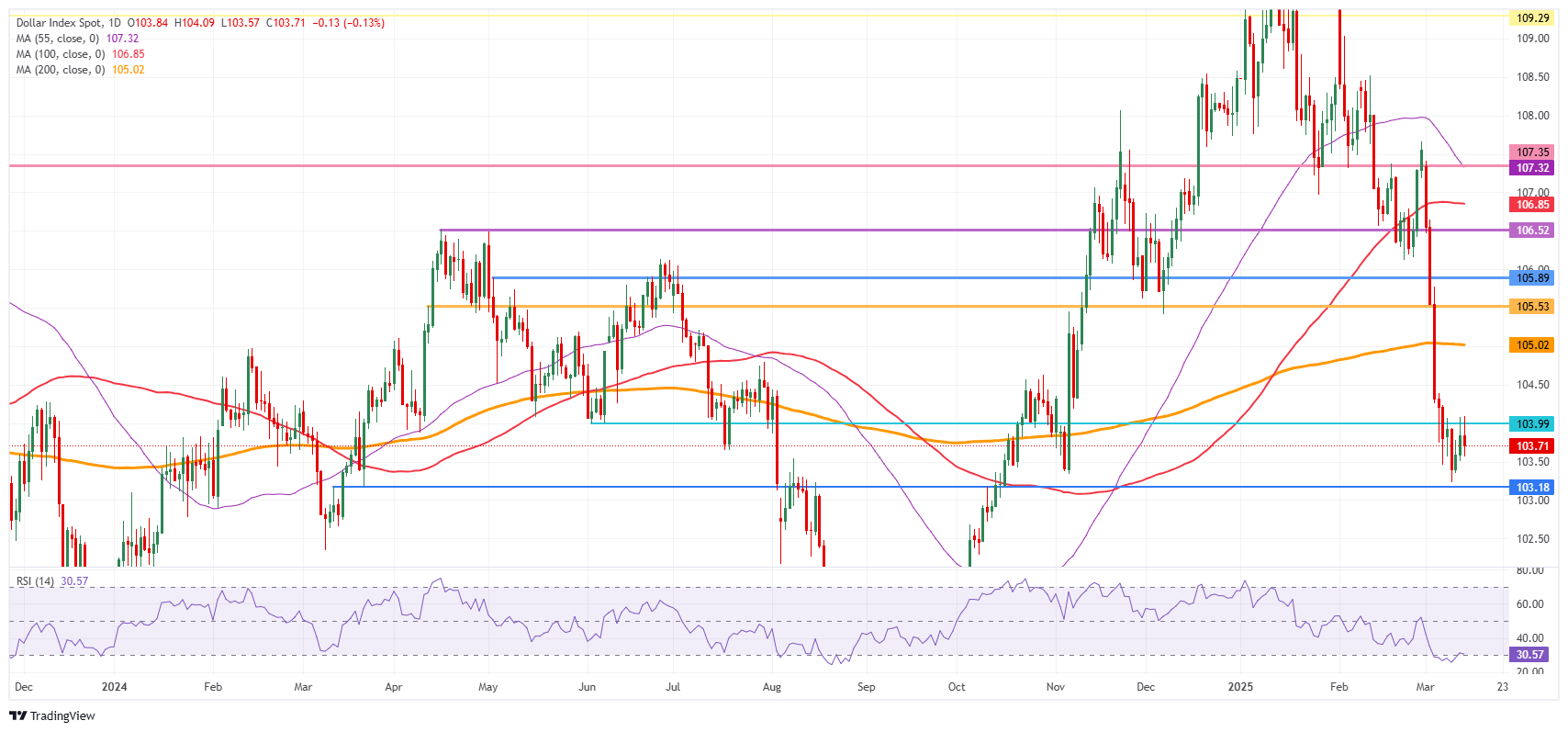
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Stuck in the middle
The US Dollar Index (DXY) shows bearish fatigue after its steep downward correction last week. Volatility in its price action completely eroded, and even the DXY stabilizes on Friday after recovering initial weekly losses. While tensions build-up ahead of reciprocal tariffs taking effect in April, it looks like the US Dollar Index might be on the verge of paring back some of the previous week’s losses when assessing the direction into next week.
Upside risk is a rejection at 104.00 that could result in more downturn. If bulls can avoid that, look for a large sprint higher towards the 105.00 round level, with the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 105.02. Once broken through that zone, a string of pivotal levels, such as 105.53 and 105.89, will present as caps.
On the downside, the 103.00 round level could be considered a bearish target in case US yields roll off again, with even 101.90 not unthinkable if markets further capitulate on their long-term US Dollar holdings.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Interest rates FAQs
Interest rates are charged by financial institutions on loans to borrowers and are paid as interest to savers and depositors. They are influenced by base lending rates, which are set by central banks in response to changes in the economy. Central banks normally have a mandate to ensure price stability, which in most cases means targeting a core inflation rate of around 2%. If inflation falls below target the central bank may cut base lending rates, with a view to stimulating lending and boosting the economy. If inflation rises substantially above 2% it normally results in the central bank raising base lending rates in an attempt to lower inflation.
Higher interest rates generally help strengthen a country’s currency as they make it a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
Higher interest rates overall weigh on the price of Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold instead of investing in an interest-bearing asset or placing cash in the bank. If interest rates are high that usually pushes up the price of the US Dollar (USD), and since Gold is priced in Dollars, this has the effect of lowering the price of Gold.
The Fed funds rate is the overnight rate at which US banks lend to each other. It is the oft-quoted headline rate set by the Federal Reserve at its FOMC meetings. It is set as a range, for example 4.75%-5.00%, though the upper limit (in that case 5.00%) is the quoted figure. Market expectations for future Fed funds rate are tracked by the CME FedWatch tool, which shapes how many financial markets behave in anticipation of future Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.


















