Australian Dollar remains under pressure as US Dollar appreciates ahead of US PPI
- The Australian Dollar depreciates despite hawkish comments by the RBA Governor Michele Bullock.
- Australia’s seasonally adjusted Unemployment Rate held steady at 4.1% in October for the third consecutive month.
- Traders are now shifting their focus to the US October Producer Price Index (PPI) data, set to be released on Thursday.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) continues its losing streak against the US Dollar (USD) following the key economic data release on Thursday. Australia's Consumer Inflation Expectations dropped to 3.8% in November, down from 4.0% in the previous month, reaching the lowest level since October 2021.
Australia’s seasonally adjusted Unemployment Rate remained steady at 4.1% in October for the third consecutive month, in line with market expectations. However, Employment Change showed only 15.9K new jobs added in October, falling short of the anticipated 25.0K.
Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) Governor Michele Bullock stated on Thursday that current interest rates are sufficiently restrictive and will remain so until the central bank is confident about inflation trends. Bullock noted the uncertainty surrounding potential actions by the US Federal Reserve and emphasized that the RBA will avoid making any hasty decisions.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the value of the US Dollar against its six major peers, hovers around 106.60, its highest level since November 2023, driven by "Trump trades" and October's US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data. Donald Trump’s victory in last week’s US presidential election fueled expectations of potentially inflationary tariffs and other measures from his upcoming administration, giving a strong boost to the Greenback.
Australian Dollar remains under pressure as US Dollar continues to gain ground
- Federal Reserve (Fed) Bank of St. Louis President Alberto Musalem commented on Wednesday that persistent inflation challenges make it difficult for the Fed to continue easing rates. Musalem redirected attention to the overall strength of the US labor market, seeking to alleviate concerns about inflation's resistance to the Fed's downward pressure efforts.
- Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City President Jeffrey Schmid highlighted potential challenges in the journey toward lowering interest rates. Schmid also criticized market participants who continue to hold out hope for a return to near-zero rates, calling their expectations unrealistic.
- US Consumer Price Index (CPI) increased by 2.6% year-over-year in October, in line with market forecasts. Meanwhile, the core CPI, which excludes the more volatile food and energy components, rose by 3.3% as expected.
- Australia's Prime Minister Anthony Albanese shared in a radio interview on Wednesday that he discussed trade with US President-elect Donald Trump during a phone call last week. Albanese informed Trump that the United States holds a trade surplus with Australia and emphasized that it is in Washington's best interest to "trade fairly" with its ally. Meanwhile, the defense minister underscored Australia's significant investment in security.
- Matthew Hassan, Senior Economist at Westpac, noted, "Consumers are feeling less pressure on their family finances, are no longer worried about further interest rate rises, and are increasingly confident in the economic outlook."
- Last week, China's latest stimulus measures fell short of investor expectations, further dampening demand prospects for Australia’s largest trading partner and weighing on the Australian Dollar. China announced a 10 trillion Yuan debt package designed to alleviate local government financing pressures and support struggling economic growth. However, the package stopped short of implementing direct economic stimulus measures.
- Morgan Stanley divides the Trump administration's macroeconomic policies into three key areas: tariffs, immigration, and fiscal measures. The report predicts that tariff policies will be prioritized, with an anticipated immediate imposition of 10% tariffs globally and 60% tariffs specifically on China.
- On Thursday, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell stated he doesn’t anticipate Trump’s potential return to the White House impacting the Fed’s near-term policy decisions. “We don’t guess, speculate, and we don’t assume what future government policy choices will be,” Powell noted after the bank decided to lower interest rates by 25 basis points to a range of 4.50%-4.75%, as expected.
Australian Dollar trades below 0.6500 due to short-term downward pressure
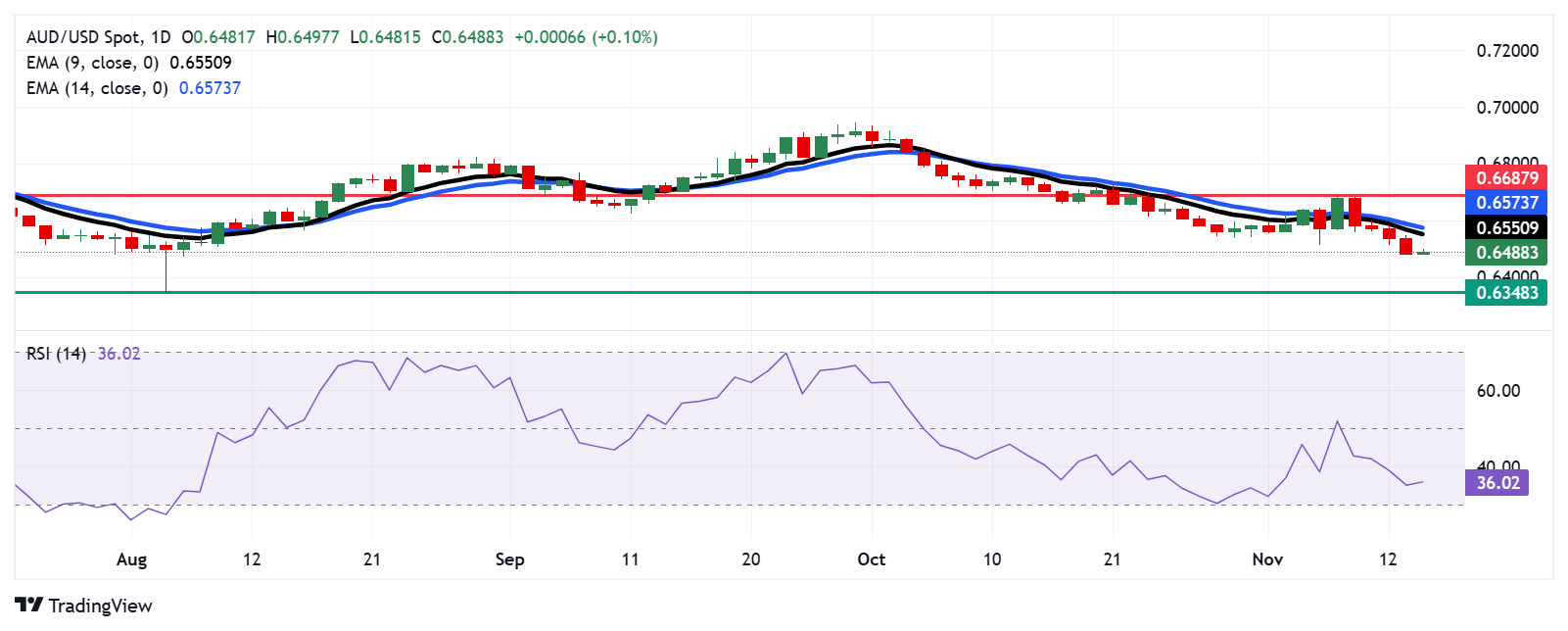
The AUD/USD pair trades near 0.6490 on Thursday. An analysis of the daily chart indicated short-term downward pressure, with the pair remaining below the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Additionally, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) is below the 50 mark, reinforcing a bearish outlook.
The AUD/USD pair may find support near the psychological level of 0.6400. A break below this level could increase downward pressure, potentially leading the pair to approach the yearly low of 0.6348, last reached on August 5.
On the upside, immediate resistance is seen at the psychological level of 0.6500. A break above this could push the AUD/USD pair toward the nine-day EMA at 0.6550, followed by the 14-day EMA at 0.6573. Clearing these EMAs may propel the pair toward its three-week high of 0.6687, with the next psychological target at 0.6700.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
Interest rates FAQs
Interest rates are charged by financial institutions on loans to borrowers and are paid as interest to savers and depositors. They are influenced by base lending rates, which are set by central banks in response to changes in the economy. Central banks normally have a mandate to ensure price stability, which in most cases means targeting a core inflation rate of around 2%. If inflation falls below target the central bank may cut base lending rates, with a view to stimulating lending and boosting the economy. If inflation rises substantially above 2% it normally results in the central bank raising base lending rates in an attempt to lower inflation.
Higher interest rates generally help strengthen a country’s currency as they make it a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
Higher interest rates overall weigh on the price of Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold instead of investing in an interest-bearing asset or placing cash in the bank. If interest rates are high that usually pushes up the price of the US Dollar (USD), and since Gold is priced in Dollars, this has the effect of lowering the price of Gold.
The Fed funds rate is the overnight rate at which US banks lend to each other. It is the oft-quoted headline rate set by the Federal Reserve at its FOMC meetings. It is set as a range, for example 4.75%-5.00%, though the upper limit (in that case 5.00%) is the quoted figure. Market expectations for future Fed funds rate are tracked by the CME FedWatch tool, which shapes how many financial markets behave in anticipation of future Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.