Gold price bulls now await sustained move beyond $2,900 mark before placing fresh bets
- Gold price regains positive traction amid the rising risk of a global trade war.
- A modest USD uptick might cap any meaningful gains for the XAU/USD pair.
- Traders might also opt to wait for the release of the US NFP report on Friday.
Gold price (XAU/USD) attracts some dip-buying during the early European session on Tuesday and turns positive for the second straight day, with bulls looking to build on the momentum beyond the $2,900 mark. Concerns about the economic fallout from US President Donald Trump's trade tariffs, which could trigger a global trade war, along with geopolitical risks, weigh on investors' sentiment. This turns out to be a key factor that continues to underpin demand for the safe-haven bullion.
Meanwhile, expectations that US President Donald Trump's trade tariffs would reignite inflation and force the Federal Reserve (Fed) to keep interest rates higher for longer help revive the US Dollar (USD) demand. This might hold back bulls from placing aggressive bets around the non-yielding Gold price and cap the upside. Investors might also opt to wait for the release of the US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report on Friday before determining the next leg of a directional move for the commodity.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price attracts safe-haven flows amid rising trade tensions
- Investors remain worried that US President Donald Trump's trade tariffs would increase price pressures and allow the Federal Reserve to stick to its hawkish stance, prompting some selling around the Gold price on Tuesday.
- Trump's tariffs on Mexico and Canada are taking effect this Tuesday, along with a new 10% levy on Chinese goods. Trump also said that reciprocal tariffs would take effect on April 2 on countries that impose duties on US products.
- Canada confirmed that it will impose retaliatory tariffs on US imports. China’s Commerce Ministry announced on Tuesday that it will slap additional tariffs of up to 15% on imports of key farm products from the US.
- This raises the risk of a global trade war and weighs on investors' sentiment, which should act as a tailwind for the safe-haven precious metal and help limit any deeper losses amid a bearish tone surrounding the US Dollar.
- The Institute for Supply Management's (ISM) Manufacturing PMI slipped to 50.3 in February from 50.9 in the previous month, while the Prices Paid Index jumped to a nearly three-year high amid worries about duties on imports.
- This comes on top of worries that Trump's trade tariffs would undermine consumer spending and fuel concerns about the outlook for the world’s largest economy. This could further lend support to the XAU/USD pair.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy's meeting with Trump ended in disaster on Friday. Furthermore, a White House official confirmed that the US has paused military aid to Ukraine, adding to the uncertainty in markets.
- The market focus will remain glued to the release of the US monthly employment details – popularly known as the Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report on Friday. The crucial data would influence the USD and the yellow metal.
Gold price could accelerate the positive move above the $2,900 mark
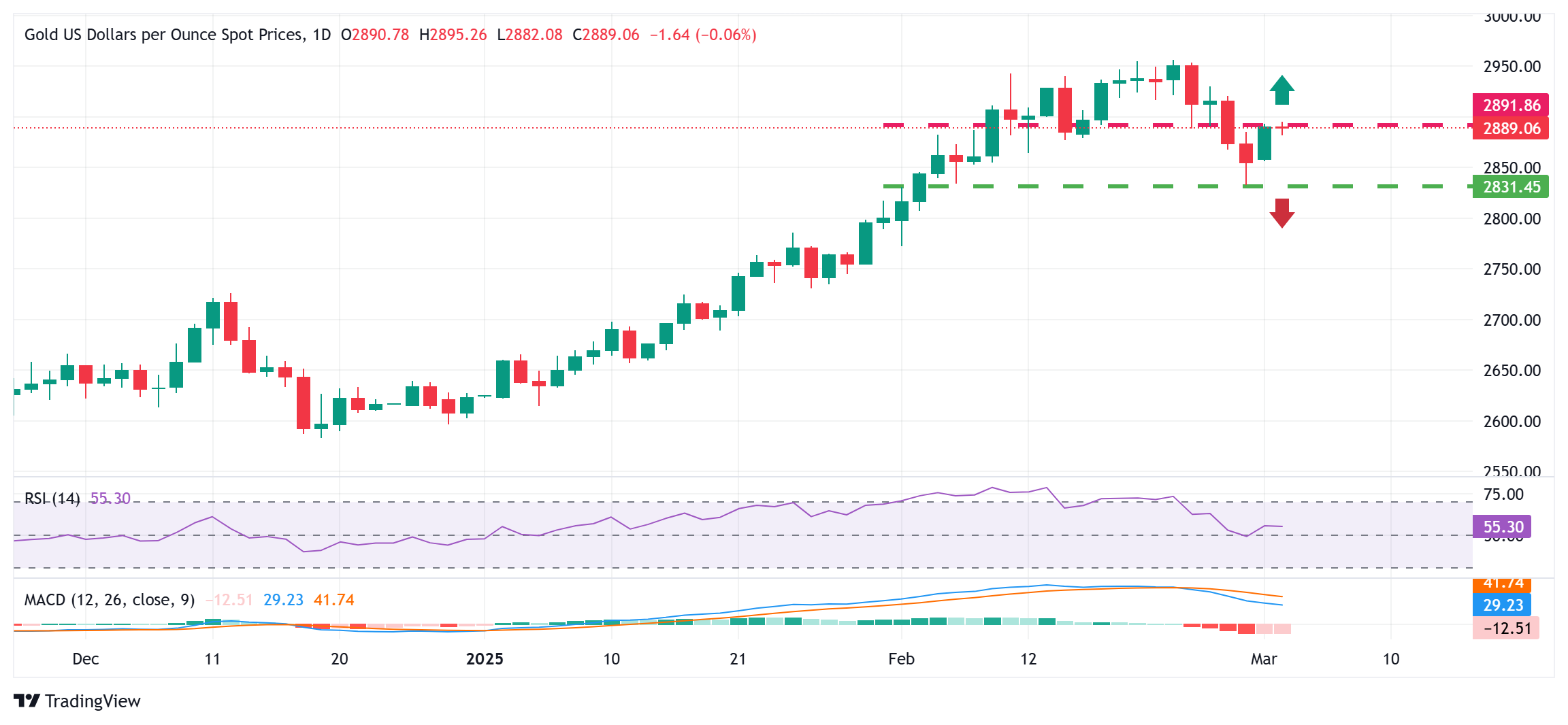
From a technical perspective, failure ahead of the $2,900 mark warrants some caution for bullish traders. That said, oscillators on the daily chart – though they have been losing traction – are holding in positive territory and support prospects for the emergence of some dip-buyers near the $2,860 immediate support. This is followed by the multi-week low, around the $2,833-2,832 region touched last Friday, below which the Gold price could accelerate the fall further towards the $2,800 round figure.
On the flip side, bulls might wait for sustained strength and acceptance back above the $2,900 mark before placing fresh bets. The subsequent move up could lift the Gold price to the $2,934 intermediate hurdle en route to the record high, around the $2,956 region touched last Monday.
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.



























