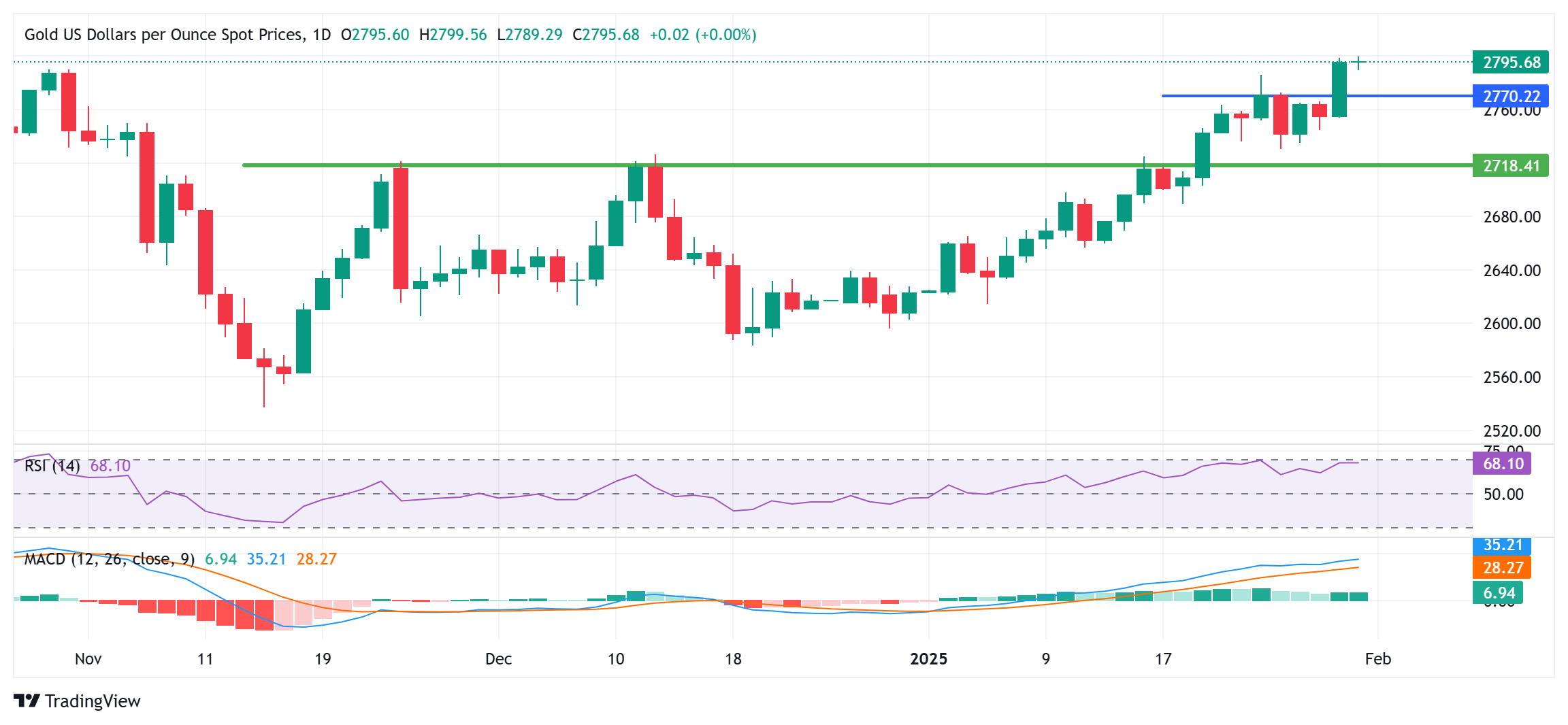
Gold price sits near record high; around $2,800 as traders await US PCE Price Index
- Gold price enters a bullish consolidation phase after touching a fresh all-time peak on Friday.
- The Fed's hawkish pause and rebounding US bond yields cap the gains for the XAU/USD pair.
- Traders now look forward to the release of the US PCE Price Index for a fresh impetus.
Gold price (XAU/USD) touches the $2,800 mark, or a fresh all-time peak during the early part of the European session, and seems poised to prolong its well-established uptrend witnessed over the past month or so. US President Donald Trump's threatened trade tariffs, along with geopolitical tensions, continue to underpin demand for the safe-haven bullion. Moreover, expectations that Trump's protectionist policies would reignite inflation turn out to be another factor that benefits the commodity's status as a hedge against rising price pressures.
This, along with a softer US Dollar (USD), supports prospects for a further near-term appreciating move for the Gold price. That said, the Federal Reserve's (Fed) hawkish pause on Wednesday and a modest recovery in the US Treasury bond yields hold back traders from placing fresh bets around the non-yielding yellow metal. Traders also seem reluctant and opt to move to the sidelines ahead of the release of the US Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index, due for release later during the North American session.
Gold price remains well supported by trade war fears, ahead of US PCE Price Index
- US President Donald Trump reiterated his threat to impose 25% tariffs on Mexico and Canada – the top two US trade partners – and warned of potential 100% tariffs if BRICS attempts to replace the US Dollar.
- Japan’s Joint Staff Office (JSO) stated that a pair of Russian Tu-95 bombers escorted by two Russian fighter aircraft carried out an eight-hour flight over the Sea of Okhotsk and Sea of Japan on Thursday.
- The US Bureau of Economic Analysis' (BEA) first estimate published on Thursday showed that Gross Domestic Product (GDP) grew at an annualized rate of 2.3% during the October-December period.
- The reading marked a notable slowdown from the 3.1% expansion recorded in the previous quarter and was below the market expectation of 2.6% and boosted demand for the safe-haven Gold price.
- Investors remain concerned that Trump's protectionist policies will reignite inflationary pressures. Adding to this, the Federal Reserve's hawkish stance provides a modest lift to the US Treasury bond yields.
- The US central bank decided to stand pat at the end of a two-day meeting on Wednesday and signaled that there would be no rush to lower borrowing costs until inflation and jobs data made it appropriate.
- The US Dollar preserves its weekly recovery gains from over a one-month low, which, along with a generally positive tone around the equity markets, keeps a lid on gains for the precious metal.
- Traders now look to the release of the US Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index – the Fed's preferred inflation gauge – for some impetus later during the North American session.
Gold price bulls have the upper hand while above the $2,773-2,772 resistance breakpoint
From a technical perspective, sustained strength and acceptance above the $2,800 mark will be seen as a fresh trigger for bulls. That said, the daily Relative Strength Index (RSI) is on the verge of breaking into the overbought zone. This makes it prudent to wait for some near-term consolidation or a modest pullback before placing fresh bullish bets around the Gold price and positioning for an extension of the strong move-up witnessed over the past month or so.
Meanwhile, any corrective slide is more likely to find decent support and remain limited near the $2,773-2,772 horizontal zone. This is followed by the $2,758-2,756 region, which if broken might prompt some long-unwinding and drag the Gold price further towards the $2,740 area en route to the $2,725-2,720 pivotal support. A convincing break below the latter could set the stage for some meaningful downside in the near term.
Interest rates FAQs
Interest rates are charged by financial institutions on loans to borrowers and are paid as interest to savers and depositors. They are influenced by base lending rates, which are set by central banks in response to changes in the economy. Central banks normally have a mandate to ensure price stability, which in most cases means targeting a core inflation rate of around 2%. If inflation falls below target the central bank may cut base lending rates, with a view to stimulating lending and boosting the economy. If inflation rises substantially above 2% it normally results in the central bank raising base lending rates in an attempt to lower inflation.
Higher interest rates generally help strengthen a country’s currency as they make it a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
Higher interest rates overall weigh on the price of Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold instead of investing in an interest-bearing asset or placing cash in the bank. If interest rates are high that usually pushes up the price of the US Dollar (USD), and since Gold is priced in Dollars, this has the effect of lowering the price of Gold.
The Fed funds rate is the overnight rate at which US banks lend to each other. It is the oft-quoted headline rate set by the Federal Reserve at its FOMC meetings. It is set as a range, for example 4.75%-5.00%, though the upper limit (in that case 5.00%) is the quoted figure. Market expectations for future Fed funds rate are tracked by the CME FedWatch tool, which shapes how many financial markets behave in anticipation of future Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.