US Dollar upbeat going into the last pieces of data for this week with Michigan Sentiment on the docket
- The US Dollar trades off support on Friday after a volatile week and trades sideways.
- Jerome Powell reassured markets and reporters on his future as Fed Chairman.
- The US Dollar index heads towards 104.50 with direction unclear going into next week.
The US Dollar (USD) is starting to tick higher going into the US trading session on Friday after founding support as investors digest the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) decision to lower its monetary policy rate by 25 basis points to the 4.50%-4.75% range on Thursday. The rate cut event completely faded to the background, with reports eager to ask if Fed Chairman Jerome Powell needs to fear for his job now that President-elect Donald Trump will come to the White House in January. Powell was quite blunt and direct in saying that he will not resign and cannot be fired, underlining that the Fed is an independent body from politics in the US.
The US economic calendar sees the release of the University of Michigan’s preliminary November report on Friday. As always, a good guide and leading indicator of how consumer sentiment in the US is holding up. The inflation expectation of US consumers in the report will be a key factor after several head economists and analysts have predicted inflation will be one of the major concerns for the Trump presidency.
Daily digest market movers: Supported until Trump takes office?
- The Federal Reserve decided on Thursday to lower its monetary policy rate by 25 basis points to the 4.50%-4.75% range after the Bank of England (BoE) made the same move towards 4.75% earlier that day.
- During the press conference after the meeting, Fed Chairman Powell was asked about possible resignations or threats to his job under President-elect Trump. Powell reiterated that the Fed is an independent institute that does not follow politics and only looks at US data and its mandates. The Fed Chairman even got annoyed at one point with the question and simply said “No!” to the question, Reuters reports.
- At 15:00 GMT, the University of Michigan will release its preliminary reading for November. Consumer Sentiment is expected to tick up to 71 from 70.5 in the previous month. Inflation expectations, which were at 3% in October, have no consensus view.
- At 16:00 GMT, Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman participates in a conversation about banking at a symposium organized by the University of Mississippi School of Business.
- European equities have a clear off-day with losses near 1% intraday. US futures are looking bleak as well ahead of the US opening bell.
- The CME FedWatch Tool is pricing in another 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the Fed at the December 18 meeting by 71.3%. A smaller 28.7% chance is for rates to remain unchanged.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 4.31%, tumbling lower from this week’s high at 4.47%.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Powell will support DXY
The US Dollar Index (DXY) eased on Thursday after its steep move higher earlier in the week. That move came on the back of comments from Fed Chairman Jerome Powell that he is here to stay and will stay even when President-elect Donald Trump takes office. This reassures markets that stability will be present on the monetary policy front, and logical action will be taken to ensure the US economy does not overheat or head into hyperinflation.
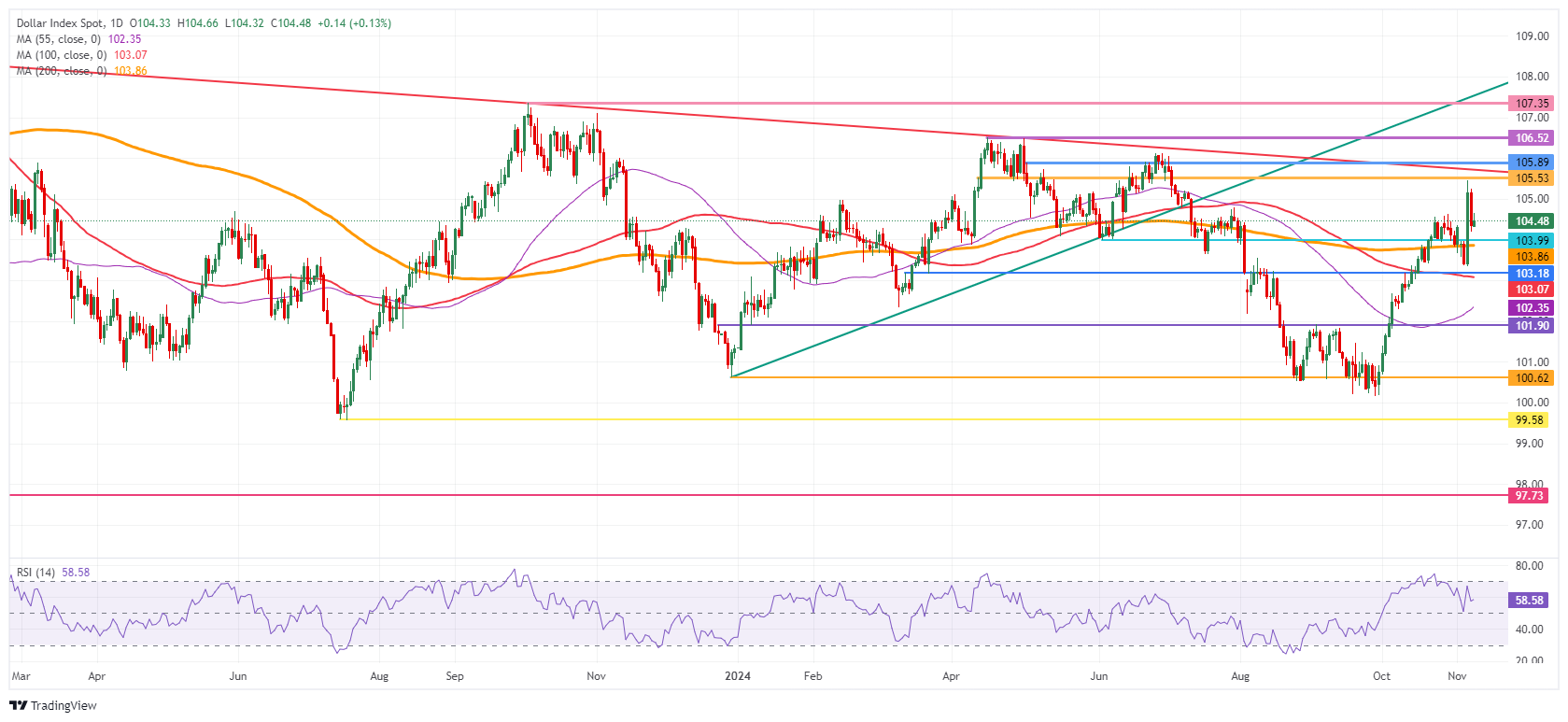
The first level to watch out for on the upside is 105.53 (April 11 high), a very firm cap resistance, with 105.89 (May 2 high) just above. Once that level is broken, 106.52, the high of April and a double top, will be the last level standing before starting to talk about 107.00.
Last week’s peak at 104.63 did not do a great job in offering some support for the fade on Thursday. On the downside, the round level of 104.00 and the 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 103.86 should refrain from sending the DXY any lower.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Employment FAQs
Labor market conditions are a key element to assess the health of an economy and thus a key driver for currency valuation. High employment, or low unemployment, has positive implications for consumer spending and thus economic growth, boosting the value of the local currency. Moreover, a very tight labor market – a situation in which there is a shortage of workers to fill open positions – can also have implications on inflation levels and thus monetary policy as low labor supply and high demand leads to higher wages.
The pace at which salaries are growing in an economy is key for policymakers. High wage growth means that households have more money to spend, usually leading to price increases in consumer goods. In contrast to more volatile sources of inflation such as energy prices, wage growth is seen as a key component of underlying and persisting inflation as salary increases are unlikely to be undone. Central banks around the world pay close attention to wage growth data when deciding on monetary policy.
The weight that each central bank assigns to labor market conditions depends on its objectives. Some central banks explicitly have mandates related to the labor market beyond controlling inflation levels. The US Federal Reserve (Fed), for example, has the dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank’s (ECB) sole mandate is to keep inflation under control. Still, and despite whatever mandates they have, labor market conditions are an important factor for policymakers given its significance as a gauge of the health of the economy and their direct relationship to inflation.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.