US Dollar holds breath after volatile start of Trump's presidency
- The US Dollar flatlines on Wednesday after two days of losses.
- Markets measuring the impact of the 10% levy over Chinese goods President Trump announced on Tuesday.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) tests the 108.00 mark and is set to head to the lower end of 107.00
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, is going nowhere and consolidates below the 108.00 mark in the European trading session on Wednesday. However, selling pressure persists after US President Donald Trump released more comments on a possible 10% levy on all Chinese imports on Tuesday. Even Europe got targeted, though tariff debates seem still ongoing.
Meanwhile, the US economic calendar is still very light. While Federal Reserve (Fed) officials remain in the blackout period ahead of the January 29 policy decision, traders focused on the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) Applications for the week ending January 17 on Wednesday. The previous week's surge of 33.3% was staggering, to say the least, and traders are intrigued to see if a Trump-effect is also playing out in the mortgage market.
Daily digest market movers: The next step
- The Mortgage Bankers Association (released on Wednesday its weekly Mortgage survey, which saw a very small 0.1% uptick in applications in the week ending January 17 compared to the previous week's 33.3% print.
- Equities are tying up with gains on Wednesday. European equities are broadly in the green, while US futures are up near 0.50% on average.
- The CME FedWatch tool projects a 55.7% chance that interest rates will remain unchanged at current levels in the May meeting, suggesting a rate cut in June. Expectations are that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will remain data-dependent with uncertainties that could influence inflation during US President Donald Trump’s term.
- The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.56% on Wednesday and has a long road to recovery if it wants to head back to last week’s peak near 4.75%.
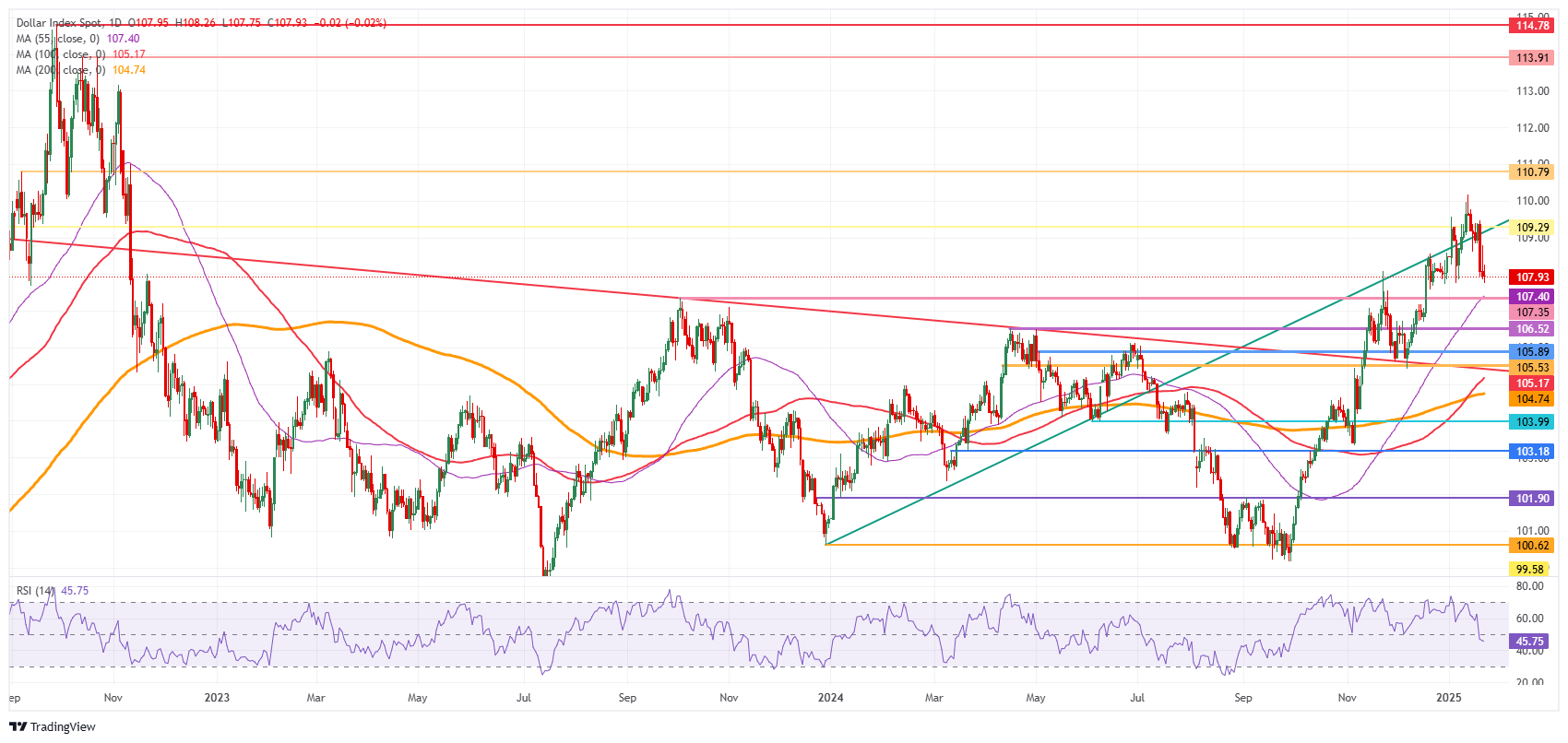
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: What when the economic data turns?
The US Dollar Index (DXY) declines further as selling pressure persists. It is not so that tariffs are triggering the US Dollar correction. Instead, it is very unclear and misty communication, where many balloons are left hanging in the air, though nothing concrete has been implemented for now.
If the recovery in the DXY wants to continue its ascent, the pivotal level to gain control of is 109.29 (July 14, 2022, high and rising trendline). Further up, the next big upside level to hit before advancing further remains at 110.79 (September 7, 2022, high). Once beyond there, it is quite a stretch to 113.91, a double top from October 2022.
On the downside, the first area to watch is 107.80-107.90, which held this week’s correction. Further down, the convergence of the high of October 3, 2023, and the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) around 107.40 should act as a double safety feature to catch any falling knives.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Central banks FAQs
Central Banks have a key mandate which is making sure that there is price stability in a country or region. Economies are constantly facing inflation or deflation when prices for certain goods and services are fluctuating. Constant rising prices for the same goods means inflation, constant lowered prices for the same goods means deflation. It is the task of the central bank to keep the demand in line by tweaking its policy rate. For the biggest central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BoE), the mandate is to keep inflation close to 2%.
A central bank has one important tool at its disposal to get inflation higher or lower, and that is by tweaking its benchmark policy rate, commonly known as interest rate. On pre-communicated moments, the central bank will issue a statement with its policy rate and provide additional reasoning on why it is either remaining or changing (cutting or hiking) it. Local banks will adjust their savings and lending rates accordingly, which in turn will make it either harder or easier for people to earn on their savings or for companies to take out loans and make investments in their businesses. When the central bank hikes interest rates substantially, this is called monetary tightening. When it is cutting its benchmark rate, it is called monetary easing.
A central bank is often politically independent. Members of the central bank policy board are passing through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed to a policy board seat. Each member in that board often has a certain conviction on how the central bank should control inflation and the subsequent monetary policy. Members that want a very loose monetary policy, with low rates and cheap lending, to boost the economy substantially while being content to see inflation slightly above 2%, are called ‘doves’. Members that rather want to see higher rates to reward savings and want to keep a lit on inflation at all time are called ‘hawks’ and will not rest until inflation is at or just below 2%.
Normally, there is a chairman or president who leads each meeting, needs to create a consensus between the hawks or doves and has his or her final say when it would come down to a vote split to avoid a 50-50 tie on whether the current policy should be adjusted. The chairman will deliver speeches which often can be followed live, where the current monetary stance and outlook is being communicated. A central bank will try to push forward its monetary policy without triggering violent swings in rates, equities, or its currency. All members of the central bank will channel their stance toward the markets in advance of a policy meeting event. A few days before a policy meeting takes place until the new policy has been communicated, members are forbidden to talk publicly. This is called the blackout period.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.