Japanese Yen consolidates in a range against USD, bears not ready to give up yet
- The Japanese Yen fails to build on the previous day's recovery from a multi-month low.
- The BoJ rate-hike uncertainty and the risk-on mood cap gains for the safe-haven JPY.
- Renewed USD buying interest and elevated US bond yields offer support to USD/JPY.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) struggles to attract any meaningful buyers on Friday and seesaws between tepid gains/minor losses against its American counterpart heading into the European session. The recent verbal intervention from Japanese authorities turns out to be a key factor lending support to the JPY, though doubts over the Bank of Japan's (BoJ) ability to hike interest rates further cap gains.
Meanwhile, hopes that Trump's policies will spur growth and inflation, to a larger extent, overshadows the Federal Reserve's (Fed) rather dovish outlook. This, in turn, acts as a tailwind for the US Treasury bond yields and contributes to keeping a lid on the lower-yielding JPY. Apart from this, the emergence of some buying around the US Dollar (USD) helps limit the downside for the USD/JPY pair.
Japanese Yen fails to build on modest intraday gains amid mixed fundamental cues
- Government data released this Friday showed that Japan's household spending fell for the second successive month, by 1.3% in September and 1.1% from the year earlier.
- This comes on top of a fall in Japan's inflation-adjusted wages for the second straight month in September and could hinder the Bank of Japan's plans to hike rates further.
- Donald Trump’s victory in the US presidential election pushed the USD/JPY pair beyond the 154.00 mark on Wednesday and prompted verbal intervention by authorities.
- Japan's Chief Cabinet Secretary, Yoshimasa Hayashi, reiterated that the government intended to closely watch moves in the FX market with a higher sense of urgency.
- Japan’s Vice Finance Minister for International Affairs and top FX official Atsushi Mimura said that the government is ready to take appropriate actions against excessive FX moves.
- Japan’s Finance Minister Katsunobu Kato on Friday that the government will closely monitor the impact of the President-elect Donald Trump's policies on the domestic economy.
- Quarterly data from the Ministry of Finance (MOF) showed this Friday that Japan spent ¥5.53 trillion on currency intervention made during the period from June 27 through July 29.
- The US Dollar attracts some dip-buying on Friday to reverse a part of Thursday's pullback from a four-month top and offer some support to the USD/JPY pair.
- The Federal Reserve lowered borrowing costs by 25 basis points on Thursday, following a jumbo rate cut in September that kicked off the policy easing cycle.
- In the post-meeting press conference, Fed Chair Jerome Powell failed to offer any cues that the central bank was likely to pause rate cuts in the near term.
- According to the CME Group's FedWatch Tool, market participants are now pricing in 75% odds the US central bank will cut interest rates again in December.
- Furthermore, traders continue to unwind some of the profitable Trump trades, which might cap any meaningful upside for the USD and the currency pair.
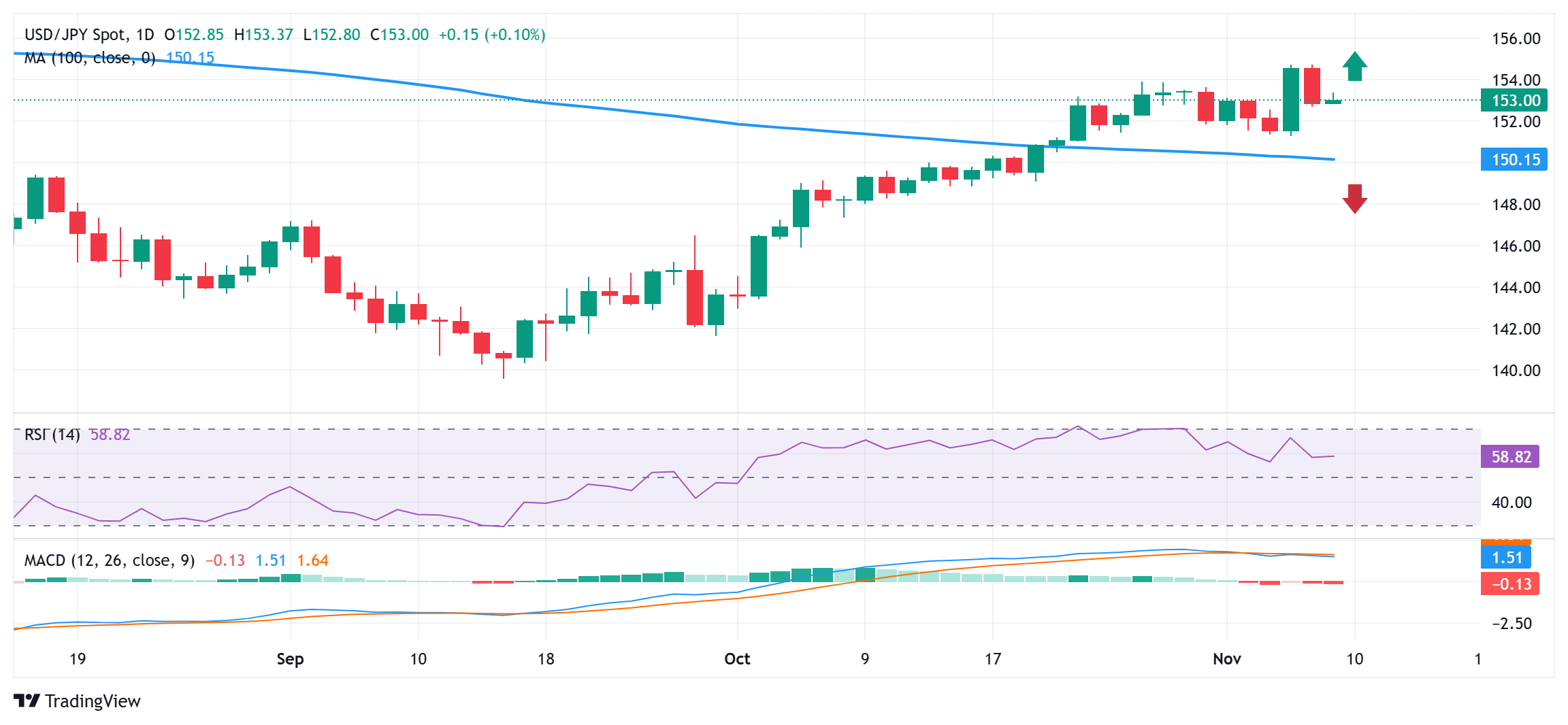
Technical Outlook: USD/JPY bulls have the upper hand while above the 200-day SMA
From a technical perspective, the overnight downfall stalled near the 152.70-152.65 horizontal support. The said area might now act as a pivotal point, below which the USD/JPY pair could accelerate the corrective decline towards the 152.00 mark en route to the 100-day Simple Moving Average (SMA), around the 151.70-151.65 region. Some follow-through selling will suggest that the recent strong move up from the September monthly swing low has run out of steam and paves the way for deeper losses.
On the flip side, the 153.50 area could act as an immediate hurdle ahead of the 153.85-153.90 supply zone. A subsequent move back above the 154.00 mark has the potential to lift the USD/JPY pair back towards the multi-month peak, around the 154.70 region touched on Thursday. The momentum could extend further toward the 155.00 psychological mark and the 155.20 zone (July 30 swing high).
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.