EUR/USD trades cautiously as investors seek more clarity on Trump's tariff plans
- EUR/USD wobbles around 1.0400 as the US Dollar gains ground amid concerns over global economic growth with Trump’s tariffs.
- ECB President Lagarde has advised that Europe should be prepared to respond to Trump’s tariff hikes.
- The Fed and the ECB are set to announce their first monetary policy decision of 2025 next week.
EUR/USD ticks lower to near 1.0400 in Thursday’s North American session as the US Dollar (USD) gains ground. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, extends its recovery to near 108.40 from the two-week low of 107.75 posted on Wednesday. The Greenback bounces back as the market sentiment turns slightly cautious, with investors assessing the consequences of United States (US) President Donald Trump’s tariffs on economic growth.
Trump has threatened 25% tariff hikes on Canada and Mexico and 10% on China, which will come into effect on February 1. He also plans to impose tariffs on Europe after accusing the bloc of being "very, very bad to us". Trump’s tariff hike approach appears to be more gradual than what market participants had anticipated. However, they would still be unfavorable to global economic growth.
On Wednesday, European Central Bank (ECB) President Christine Lagarde commented on CNBC that Trump’s decision not to swiftly impose tariffs was a "smart approach" because blanket levies don’t necessarily give you the “results that you expect." Lagarde warned that Europe must “anticipate what will happen” and be “prepared in order to respond,” as Trump’s tariffs would be “selective” and “focused.”
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD consolidates as investors await Fed-ECB policy
- EUR/USD ranges on Thursday, with investors focusing on flash private Eurozone and the US Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) data for January, which will be published on Friday. Eurozone HCOB PMI report, compiled by S&P Global, is expected to show that overall business activity continued to contract but at a slower pace. The HCOB Composite PMI is estimated to come in slightly higher at 49.7, compared to 49.6 in December.
- On the US front, economists expect overall business activity to have expanded almost at a steady pace. Activities in the manufacturing sector are estimated to have contracted again but at a slower pace. Meanwhile, the service sector activity is expected to expand moderately.
- Investors should also brace for significant volatility in the next week as the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the ECB will announce their first monetary policy decisions this year. The Fed is certain to keep interest rates in the range of 4.25%-4.50%, according to the CME FedWatch tool. Meanwhile, traders have fully priced in a 25-basis points (bps) interest rate reduction by the ECB.
- Traders also expect the ECB to cut its Deposit Facility rate in each of its next four policy meetings. ECB policymaker and Finnish central bank governor Olli Rehn said on Wednesday that he is now confident that “inflation will stabilize at the target as predicted” and monetary policy will “stop being restrictive” in the near future. However, he refrained from endorsing market expectations and argued that policy decisions will be determined meeting by meeting.
Euro PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies today. Euro was the strongest against the Swiss Franc.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.10% | 0.09% | -0.05% | 0.14% | 0.15% | 0.16% | 0.15% | |
| EUR | -0.10% | -0.02% | -0.16% | 0.04% | 0.04% | 0.03% | 0.05% | |
| GBP | -0.09% | 0.02% | -0.15% | 0.05% | 0.06% | 0.07% | 0.06% | |
| JPY | 0.05% | 0.16% | 0.15% | 0.18% | 0.21% | 0.17% | 0.19% | |
| CAD | -0.14% | -0.04% | -0.05% | -0.18% | 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.00% | |
| AUD | -0.15% | -0.04% | -0.06% | -0.21% | -0.02% | 0.00% | -0.01% | |
| NZD | -0.16% | -0.03% | -0.07% | -0.17% | -0.02% | -0.01% | -0.01% | |
| CHF | -0.15% | -0.05% | -0.06% | -0.19% | -0.01% | 0.01% | 0.00% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
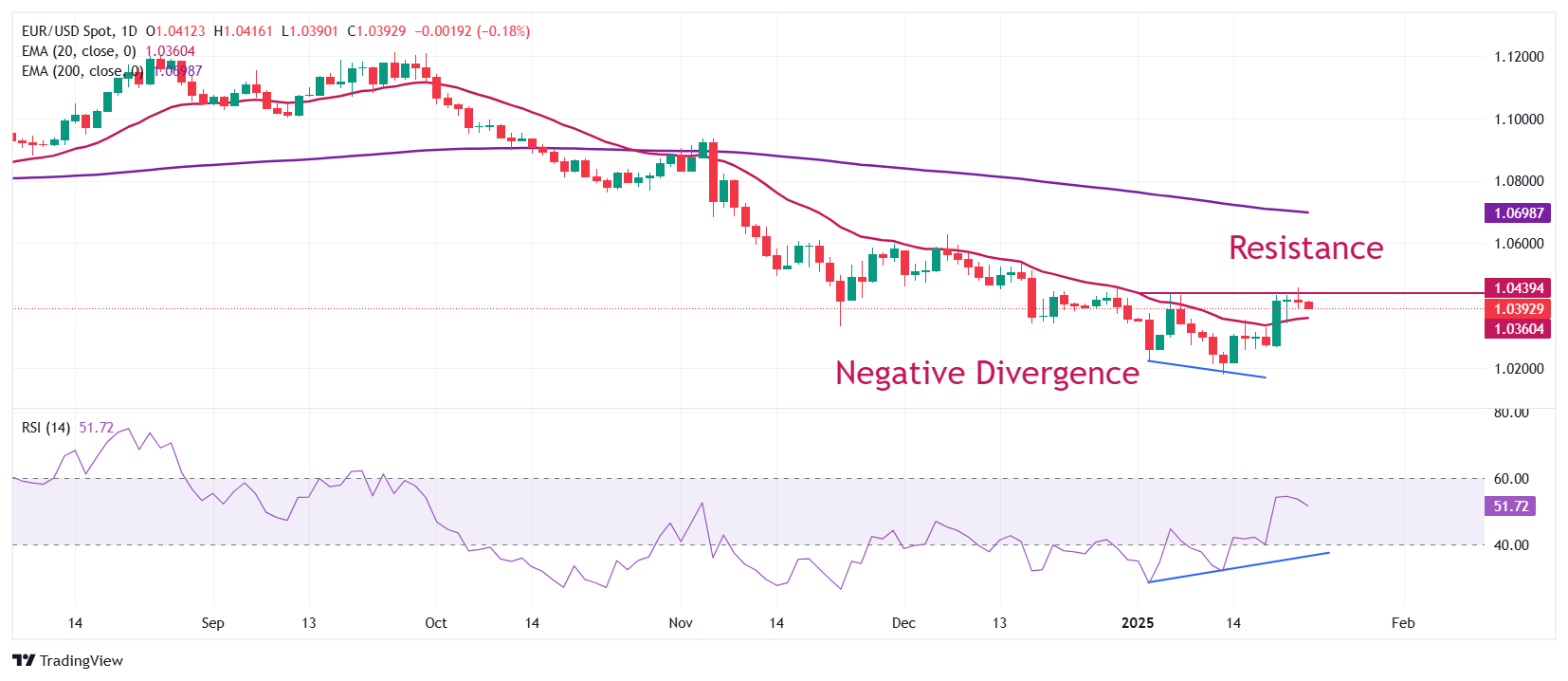
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD falls back from 1.0460
EUR/USD struggles to extend its recovery above the immediate resistance of 1.0460, which was initiated from a two-year low of 1.0175 reached on January 13. The major currency pair bounced back after a divergence in momentum and price action. The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) formed a higher low, while the pair made lower lows.
The near-term outlook of the shared currency pair has improved as it holds above the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.0360. Meanwhile, the longer-term outlook is still bearish as the 200-day EMA at 1.0700 is sloping downwards.
Looking down, the January 13 low of 1.0175 will be the key support zone for the pair. Conversely, the psychological resistance of 1.0500 will be the key barrier for the Euro bulls.
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.