US Dollar set to close off week positive despite uncertainty over the weekend on tariff threat
- The US Dollar consolidates ahead of this week's close.
- The weekend is expected to be an eventful one with Saturday, the US being set to impose tariffs on Mexico and Canada.
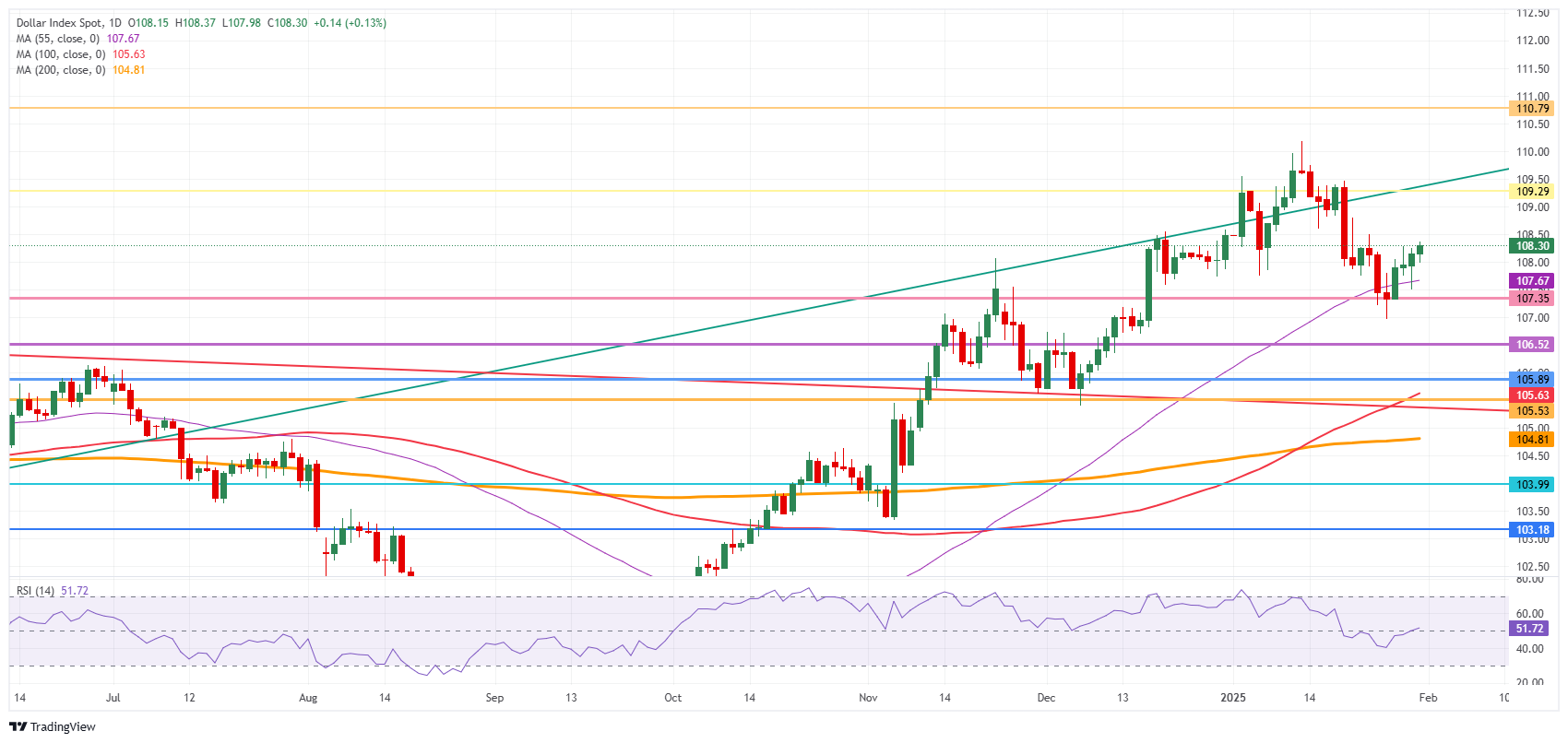
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) moves further away from 108.00 and resides near the fresh weekly high at 108.37.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar against six major currencies and currently trades at 108.35 at the time of writing, is heading higher on Friday after receiving quite a few tailwinds just ahead of the weekend. The first tailwind comes from US President Donald Trump, who announced a first wave of tariffs on Mexico and Canada. The Trump administration will impose 25% tariffs on about $900 billion in goods from both Canada and Mexico, Bloomberg reports. The US President also threatened to impose 100% tariffs on BRICS nations if they try to replace the US Dollar with a new currency in international trade.
The second tailwind comes from the rate differential between the US and several other countries. For example, this Friday the German inflation release boosted rate cut bets for the European Central Bank (ECB). This drives a bigger wedge between US yields and European ones, fueling a stronger US Dollar.
Unfortunately, the recent release of the Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) data for December was unable to further widen that rate differential. With all element roughly in line of expectations, the PCE release turned into a non-event.
Daily digest market movers: Monday might be tricky
- Asian markets remain quiet this week due to the Lunar New Year, which started on Tuesday, with Chinese traders returning to the markets on February 5.
- Volatility and nervousness are expected at the opening trade on Monday if US President Trump finally unleashes 25% tariffs on Canada and Mexico.
- Trump reiterated on Thursday his threat of imposing 100% tariffs on BRICS nations if they try to replace the US Dollar (USD) with a new currency in international trade. Trump posted on TruthSocial: “We are going to require a commitment from these seemingly hostile countries that they will neither create a new BRICS currency, nor back any other currency to replace the mighty US Dollar or, they will face 100% tariff,” and continued “there is no chance that BRICS will replace the US Dollar in international trade, or anywhere else, and any country that tries should say hello to tariffs, and goodbye to America!”
- US Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index data for December has been released:
- Monthly headline PCE ticked up 0.2% from 0.1% in November, as expected.
- Monthly core PCE jumped to 0.3% from 0.1% the previous month, in line with estimates.
- Tthe Chicago Purchasing Managers’ Index for January came in at 39.5, a marginal miss on the 40 expected, coming from 36.9 in the prior reading.
- Despite the tariff threat, equities are positive with the US equity futures set for a positive open at the New York Opening Bell.
- The CME FedWatch tool projects an 82.0% chance for no change in the Fed’s policy rate for its next meeting on March 19.
- The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.51%, bouncing higher after hitting a fresh January low at 4.484% on Thursday.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Risks are nearing
The US Dollar Index (DXY) will face a shaky weekend while markets remain closed for business until Monday morning in Asia. With tariffs imposed on Canada and Mexico as earliest as Saturday, traders will be unable to move positions until Asian markets open, which means volatility is set to surge. Once the European session kicks in,the dust will start to settle on whichever event takes place over the weekend, with the DXY expected to remain caught between 107.30 to the downside and 109.30 on the upside.
Once 108.00 level has been acquired, the next level to pare back earlier losses is 109.30 (July 14, 2022, high and rising trendline). Further up, the next upside level to hit before advancing further remains at 110.79 (September 7, 2022, high).
On the downside, the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 107.67 and the October 3, 2023, high at 107.35 acts as a double support to the DXY price. For now, that looks to be holding, though the Relative Strength Index (RSI) still has some room for the downside. Hence, rather look for 106.52 or even 105.89 as better levels.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Central banks FAQs
Central Banks have a key mandate which is making sure that there is price stability in a country or region. Economies are constantly facing inflation or deflation when prices for certain goods and services are fluctuating. Constant rising prices for the same goods means inflation, constant lowered prices for the same goods means deflation. It is the task of the central bank to keep the demand in line by tweaking its policy rate. For the biggest central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BoE), the mandate is to keep inflation close to 2%.
A central bank has one important tool at its disposal to get inflation higher or lower, and that is by tweaking its benchmark policy rate, commonly known as interest rate. On pre-communicated moments, the central bank will issue a statement with its policy rate and provide additional reasoning on why it is either remaining or changing (cutting or hiking) it. Local banks will adjust their savings and lending rates accordingly, which in turn will make it either harder or easier for people to earn on their savings or for companies to take out loans and make investments in their businesses. When the central bank hikes interest rates substantially, this is called monetary tightening. When it is cutting its benchmark rate, it is called monetary easing.
A central bank is often politically independent. Members of the central bank policy board are passing through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed to a policy board seat. Each member in that board often has a certain conviction on how the central bank should control inflation and the subsequent monetary policy. Members that want a very loose monetary policy, with low rates and cheap lending, to boost the economy substantially while being content to see inflation slightly above 2%, are called ‘doves’. Members that rather want to see higher rates to reward savings and want to keep a lit on inflation at all time are called ‘hawks’ and will not rest until inflation is at or just below 2%.
Normally, there is a chairman or president who leads each meeting, needs to create a consensus between the hawks or doves and has his or her final say when it would come down to a vote split to avoid a 50-50 tie on whether the current policy should be adjusted. The chairman will deliver speeches which often can be followed live, where the current monetary stance and outlook is being communicated. A central bank will try to push forward its monetary policy without triggering violent swings in rates, equities, or its currency. All members of the central bank will channel their stance toward the markets in advance of a policy meeting event. A few days before a policy meeting takes place until the new policy has been communicated, members are forbidden to talk publicly. This is called the blackout period.
(This story was corrected on January 31 at 13:15 GMT to say 'The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.524%, bouncing higher after hitting a fresh January low at 4.484% on Thursday.', not ' at 4.484% on xxx.')
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.