Gold flirts with more upside after nervous session on Bessent and Trump comments
- Gold’s all-time high currently resides at $2,882.35, printed on Wednesday.
- Earlier losses are being turned around to gains for Gold this Thursday.
- A sixth straight day of gains could be in the works if Gold is able to eke out another positive close.
Gold’s price (XAU/USD) has erased earlier losses from this Thursday and bounces back up, entering its sixth day of gains in its February rally. The slide was mainly triggered by comments from US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, who said that the Trump administration's focus is on bringing down 10-year Treasury yields, not the Federal Reserve's (Fed) benchmark short-term interest rate, Bloomberg reports.
On the economic data front, all eyes will be on the Bank of England monetary policy decision, where a 25 basis point (bps) interest rate cut was applied, to 4.50% after cutting it by 50 bps throughout 2024. The fact that two members voted for a 50 basis points rate cut, fuels further belief for the Federal Reserve to cut more than what markets currently project. Besides that, Federal Reserve (Fed) Governor Christopher Waller, San Francisco Fed President Mary Daly and Dallas Fed President Lorie Logan will speak later this Thursday, ahead of Friday’s Nonfarm Payrolls data release.
Daily digest market movers: Easing and soothing
- Comments from US President Donald Trump on Gaza and a new nuclear deal with Iran are soothing the tail risk element in the markets, which makes investors pare back some positions in Gold, Bloomberg reports. Trump is also expected to present a plan next week to end the war in Ukraine, which will help to ease the risk premium further.
- Commodity markets are poised to break out of a two-year slump as a rally in precious metal and agriculture prices takes place. The Bloomberg Commodity Total Return Index, which trades a basket of 24 energy, metals, and agricultural futures, has already jumped 5.9 percent this year to its highest level since the end of 2022 – which was a golden year for raw materials as economies returned from COVID-19 hibernation and the war in Ukraine wreaked havoc on supply chains, Bloomberg reports.
- Gold in the Bank of England vault is trading at a discount to the wider market, as fears over potential Trump’s tariffs spark a scramble for bullion that’s resulting in weeks-long queues to withdraw metal, Reuters reports.
- The Bank of England (BoE) has released its monetary policy decision. As expected a 25 basis point (bps) rate cut was applied to 4.50% from 4.75%. The vote split was 7 in favor for a 25 basis point rate cut against 2 votes for a 50 basis points rate cut.
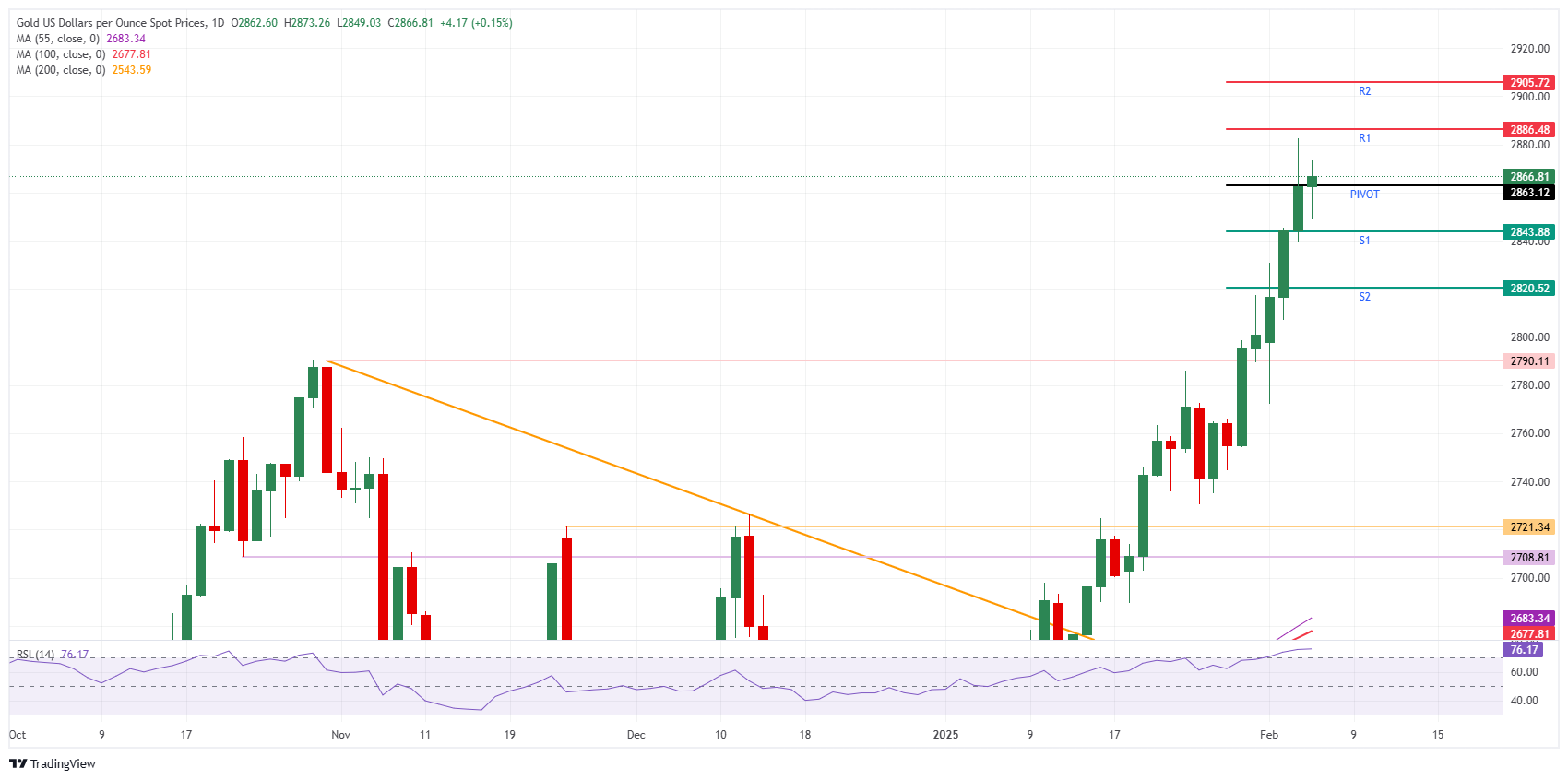
Technical Analysis: No new high for today
Markets need to change their stance quite quickly, which means that Gold is not in the sweet spot this Thursday. ‘Peaceful’ comments from US President Donald Trump are taking markets by surprise and supporting a more risky stance, which means safe havens are out of favour. With Gold being clearly one of those, selling pressure on Thursday could persist until a contradictory headline or comment comes out.
The S1 support level on Thursday is the first nearby support at $2,8343. From there, S2 support should come in at $2,820. In case of a correction, the bigger $2,790 level (the previous high of October 31, 2024) should be able to catch any falling knives.
On the upside, R1 resistance comes in at $2,886, just slightly above the current all-time high. In case the rally can pick up where it left off, the upside level to beat in terms of daily pivotal levels is R2 resistance near $2,905 after breaking above $2,900.
XAU/USD: Daily Chart
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.