Mexican Peso hoovers near 20.50 shrugs off US inflation data
- Mexican Peso weighed by hot US inflation, Fed’s rate-cut hopes dwindle
- US inflation jumps past 3%, delaying Fed rate-cut expectations until September.
- Fed Chair Powell signals restrictive policy will persist as core prices remain strong.
- MXN gains despite lack of local economic data; Mexico-US steel tariff talks ahead.
The Mexican Peso (MXN) erased some of its earlier gains against the US Dollar (USD) after inflation in the United States (US) spiked above forecasts, which would prevent the Federal Reserve (Fed) from easing policy. The USD/MXN pair trades at 20.53, vitually unchanged.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) in January jumped above the 3% YoY threshold for the first time in six months, indicating that the Fed’s job of tackling inflation is not done, as shown by US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data. Core prices also increased, justifying the Fed’s decision to hold rates at the January meeting.
After the US CPI release, the swaps market speculated that the Fed would not cut rates until the September meeting. December’s fed funds rate futures contract shows the market is pricing 29.5 basis points (bps) of easing towards the end of the year.
Meanwhile, Fed Chair Jerome Powell testified against the US House of Representatives. He commented that core prices remain strong and that the Fed must wait to see monetary policy's effects. Powell acknowledged that the job on inflation was not done and wanted to keep policy restrictive.
The economic docket remains absent in Mexico, yet President Claudia Sheinbaum said that Mexico and the US will discuss steel tariffs later this week. In the US, the schedule will feature the release of the Producer Price Index (PPI), Initial Jobless Claims, Retail Sales, and Industrial Production.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso ignores US inflation data
- Mexico’s economic docket remains absent, yet deterioration in the automobile industry and worse-than-expected Industrial Production figures hint the economy is in worse shape than expected.
- This and US President Donald Trump's trade rhetoric on Mexico would be headwinds for the Mexican currency.
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI) surpassed 3% YoY for the first time since June 2024, with the month-over-month (MoM) figures increasing by 0.5%, up from December's 0.4%.
- Excluding volatile items, the core CPI rose by 3.3% YoY from 3.2%, and monthly, it expanded by 0.4%, an increase from the previous 0.2% and exceeding the estimated 0.3%.
- Trade disputes between the US and Mexico remain in the boiler room. Although the countries found common ground previously, USD/MXN traders should know that there is a 30-day pause and that tensions could arise toward the end of February.
- Money market fed funds rate futures are pricing in 28.5 basis points (bps) of easing by the Fed in 2025.
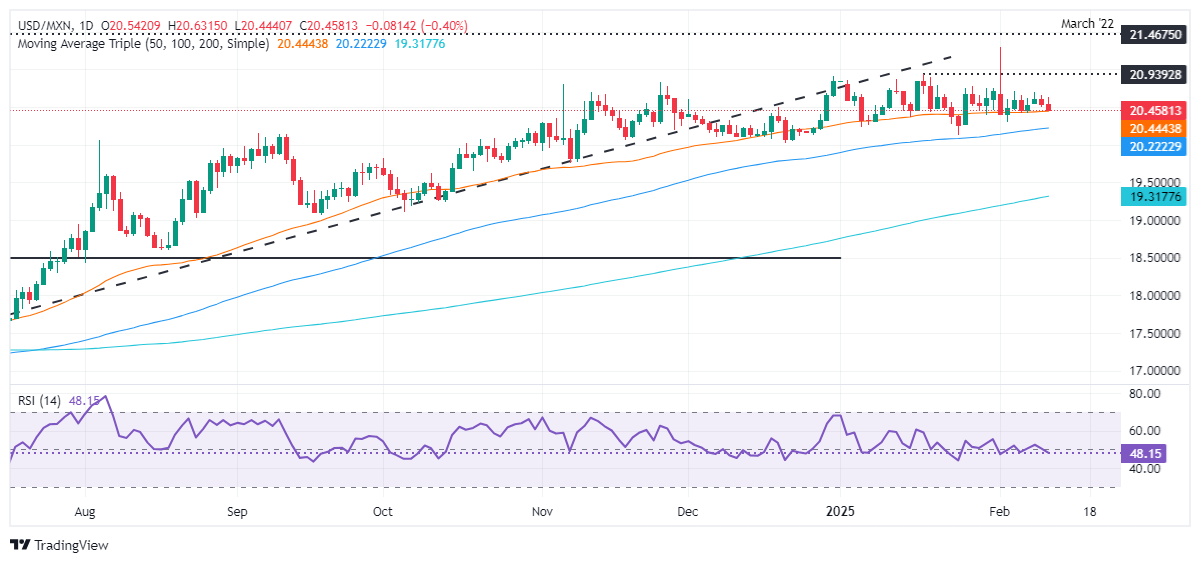
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso consolidates, awaiting fresh catalyst
USD/MXN has fallen toward the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 20.46, which, if broken, could pave the way for a retracement. Price action suggests the exotic pair has consolidated near the 20.40 – 20.68 area during the last five days, with momentum slightly tilted to the downside as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) turned bearish.
A drop of USD/MXN below 20.40 would favor a test of the 100-day SMA at 20.22, exposing the critical 20.00 figure. If surpassed, the exotic pair could aim toward 19.50 and eye a test of the 200-day SMA at 19.26.
In the meantime, if buyers clear 20.68, the next resistance would be the January 17 high at 20.90. Once surpassed, the next stop would be 21.00, followed by the year-to-date (YTD) at 21.29.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.