Japanese Yen extends its intraday descent after BoJ Governor Ueda's remarks
- The Japanese Yen attracts some sellers following the release of softer domestic data.
- A modest USD recovery from a multi-month trough further lends support to USD/JPY.
- The JPY adds to its intraday losses in reaction to BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda's remarks.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) adds to its intraday losses following Bank of Japan (BoJ) Governor Kazuo Ueda's comments at the post-meeting press conference, saying that uncertainties surrounding Japan's economy remain high. Apart from this, weaker-than-expected domestic data released earlier this Wednesday turns out to be another factor undermining the JPY. This, along with a modest US Dollar (USD) bounce from a multi-month low, pushes the USD/JPY pair to the 150.00 psychological mark, or a two-week high during the early European session.
Meanwhile, traders are still pricing in the possibility that the BoJ will hike interest rates in 2025 and the bets were reaffirmed by positive results from Shunto spring wage negotiations. In contrast, the Federal Reserve (Fed) is expected to cut rates several times this year, which has been a key factor behind the recent sharp narrowing of the US-Japan rate differential. This, in turn, should cap the USD and limit losses for the lower-yielding JPY, warranting some caution before positioning for any further move up for the USD/JPY pair ahead of the Fed decision.
Japanese Yen remains depressed during BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda's post-meeting presser
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ) announced on Wednesday that it maintained the short-term interest rate target in the range of 0.40%- 0.50% after concluding its two-day monetary policy review meeting. In the accompanying policy statement, the central bank noted that the uncertainty surrounding Japan's economy, prices remains high.
- In the post-meeting press conference, BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda said that the central bank will guide policy from standpoint of sustainably, stably achieving price target and keep adjusting degree of easing if outlook is to be realised. This, however, does little to provide any meaningful impetus to the Japanese Yen.
- Data released earlier this Wednesday showed that Japan's Trade Balance shifted to a surplus of ¥584.5 billion in February from a deficit of ¥415.43 billion in the same month a year earlier. The reversal was driven by a surge in exports, which increased by 11.4% YoY, and a larger-than-expected fall of 0.7% in imports.
- Meanwhile, Japan’s Machinery Orders fell 3.5% MoM in January 2025, significantly worse than the 1.2% decline registered in the previous month. On an annual basis, Machinery Orders rose 4.4% during the reported month, slightly above December’s 4.3% increase, though the reading was below the 6.9% forecast.
- Adding to this, a Reuters Tankan poll indicated that business sentiment among Japanese manufacturers worsened for the first time in three months during March amid concerns about US tariff policies and weakness in China’s economy. In fact, the manufacturers’ index came in at -1, down from +3 in February.
- The results of Japan's annual spring labor negotiations, which concluded on Friday, showed that firms largely agreed to union demands for strong wage growth for the third straight year. This could boost consumer spending and contribute to rising inflation, giving the BoJ headroom to keep hiking rates.
- Investors on Wednesday will also focus on the outcome of a two-day FOMC monetary policy meeting, due to be announced later during the US session. Heading into the key central bank event risks, a modest US Dollar recovery from a multi-month low pushes the USD/JPY pair back above mid-149.00s.
USD/JPY could accelerate the positive move once the 150.00 mark barrier is cleared decisively
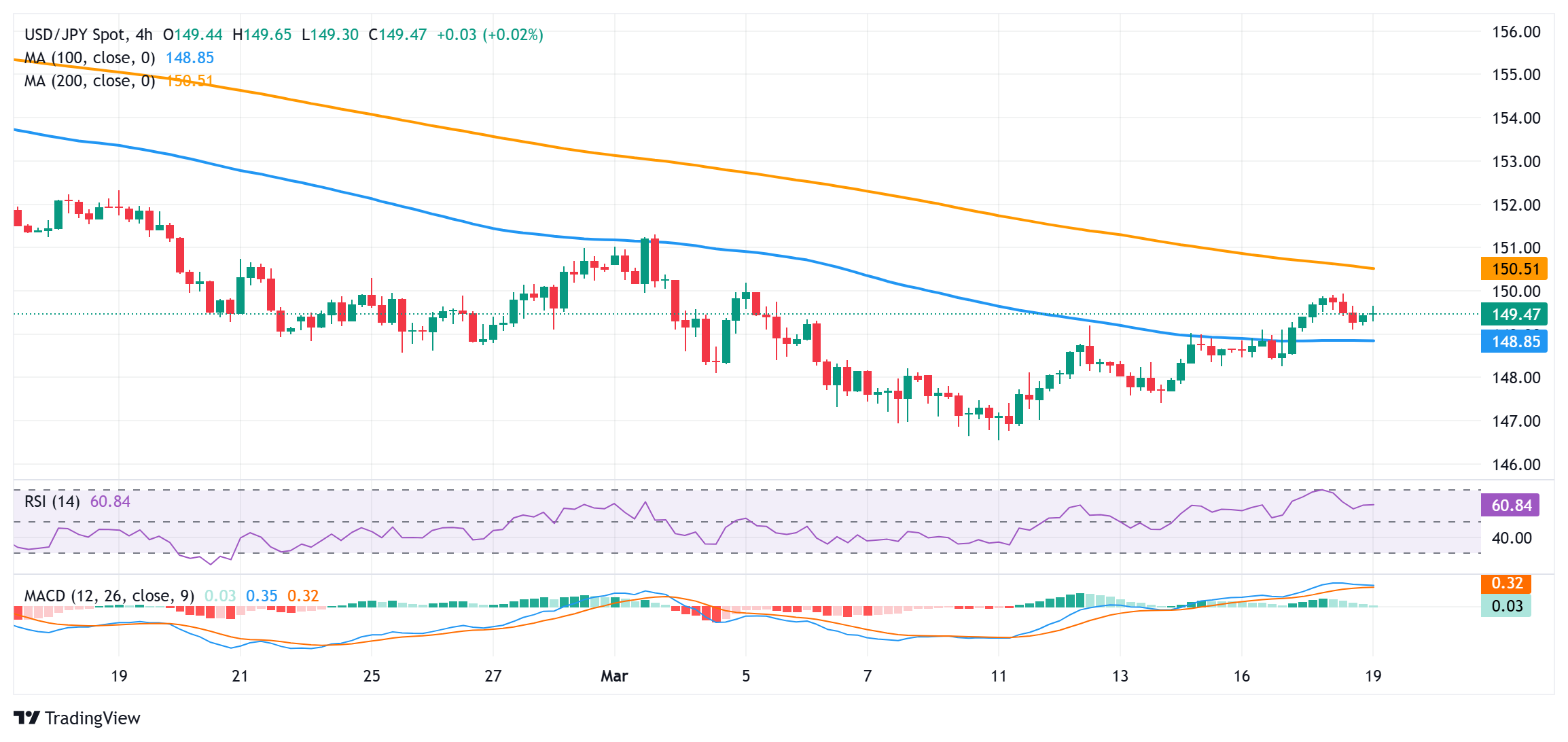
From a technical perspective, the recent breakout above the 100-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) on the 4-hour chart was seen as a key trigger for bulls. Moreover, oscillators on the said chart are holding comfortably in positive territory and support prospects for additional gains. That said, the overnight failure ahead of the 150.00 psychological mark warrants some caution. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for a sustained strength beyond the said handle before positioning for a move towards the 150.75-150.80 region, or the 200-period SMA on the 4-hour chart, en route to the 151.00 round figure.
On the flip side, the 149.20 area, followed by the 149.00 mark and the 148.80 region (100-period SMA on the 4-hour chart) should act as immediate support. A convincing break below the latter will suggest that the recent move-up witnessed over the past week or so has run out of steam and drag the USD/JPY pair to the 148.25-148.20 support en route to the 148.00 mark. The downward trajectory could extend further towards the 147.70 area, 147.20 region, and the 147.00 mark before spot prices eventually drop to retest a multi-month low, around the 146.55-146.50 region touched on March 11.
Japanese Yen PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Japanese Yen (JPY) against listed major currencies today. Japanese Yen was the strongest against the Australian Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.22% | 0.20% | 0.22% | 0.11% | 0.24% | 0.24% | 0.00% | |
| EUR | -0.22% | -0.03% | 0.02% | -0.11% | 0.03% | 0.02% | -0.21% | |
| GBP | -0.20% | 0.03% | 0.04% | -0.08% | 0.06% | 0.04% | -0.20% | |
| JPY | -0.22% | -0.02% | -0.04% | -0.13% | 0.03% | -0.00% | -0.22% | |
| CAD | -0.11% | 0.11% | 0.08% | 0.13% | 0.15% | 0.15% | -0.12% | |
| AUD | -0.24% | -0.03% | -0.06% | -0.03% | -0.15% | -0.02% | -0.22% | |
| NZD | -0.24% | -0.02% | -0.04% | 0.00% | -0.15% | 0.02% | -0.24% | |
| CHF | -0.00% | 0.21% | 0.20% | 0.22% | 0.12% | 0.22% | 0.24% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Japanese Yen from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent JPY (base)/USD (quote).
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.























