EUR/USD corrects as US Dollar rebounds ahead of Fed's policy decision
- EUR/USD faces selling pressure near 1.0950 as the US Dollar bounces back ahead of the Fed’s monetary policy decision.
- The Fed is expected to keep interest rates steady in the range of 4.25%-4.50%.
- The Euro drops despite German leaders agreed on increasing the borrowing limit in the lower house of Parliament.
EUR/USD corrects to near 1.0900 in Wednesday’s New York session after posting a fresh five-month high near 1.0955 the previous day. The major currency pair weakens as the US Dollar (USD) recovers ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) interest rate decision at 18:00 GMT. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, jumps to near 103.70 after revisiting a five-month low around 103.20 on Tuesday.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, the Fed is almost certain to keep borrowing rates steady in the range of 4.25%-4.50%. This would be the second straight policy meeting in which the Fed will leave interest rates unchanged.
Traders have remained increasingly confident about the Fed maintaining a status quo on Wednesday as officials have been arguing in favor of maintaining a “wait and see” approach until they get clarity over the United States (US) economic outlook under the leadership of President Donald Trump.
Market participants expect that Donald Trump’s tariff policies could result in a resurgence in inflationary pressures in the near term as the impact of higher import duties will be borne by US importers who will pass on the impact to consumers.
Apart from the interest rate decision, investors will also focus on the Fed’s dot plot, which shows policymakers’ collective forecast for the interest rate outlook in the medium and longer term. In the December meeting, Fed officials projected two interest rate cuts in 2025.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD weakens as Euro declines despite German debt deal approves
- A corrective move in the EUR/USD pair from the five-month high is also driven by the Euro's (EUR) underperformance against its peers, except against antipodeans. The Euro drops even though German leaders approved likely Chancellor Frederich Merz’s debt restructuring plan on Tuesday at Bundestag lower house Parliament, aiming to stimulate economic growth and boost defense spending.
- Market participants expect that an end to German fiscal conservatism after over a decade will be inflationary and pro-growth for the economy. Such a scenario will force the European Central Bank (ECB) to turn cautious about the current monetary expansion cycle. The ECB has reduced interest rates six times since June 2024.
- Also, investors expect that US President Trump’s tariff agenda could accelerate price pressures in the Eurozone. On Tuesday, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent confirmed in an interview with Fox Business that each country will receive a number on “April 2” that we believe represents their “tariffs”.
- On the geopolitical front, US President Trump and Russian leader Vladimir Putin agreed to seek an inmediate 30-day ceasefire between Russia and Ukraine on energy and infrastructure targets.
- "We agreed to an immediate Ceasefire on all Energy and Infrastructure, with an understanding that we will be working quickly to have a Complete Ceasefire and, ultimately, an END to this very horrible War between Russia and Ukraine," Trump said in a post on Truth Social on Tuesday.
Euro PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies today. Euro was the strongest against the New Zealand Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | 0.43% | 0.24% | 0.42% | 0.13% | 0.42% | 0.54% | 0.38% | |
| EUR | -0.43% | -0.20% | 0.00% | -0.30% | 0.00% | 0.12% | -0.05% | |
| GBP | -0.24% | 0.20% | 0.21% | -0.10% | 0.20% | 0.31% | 0.13% | |
| JPY | -0.42% | 0.00% | -0.21% | -0.32% | -0.02% | 0.08% | -0.07% | |
| CAD | -0.13% | 0.30% | 0.10% | 0.32% | 0.31% | 0.43% | 0.24% | |
| AUD | -0.42% | -0.01% | -0.20% | 0.02% | -0.31% | 0.11% | -0.04% | |
| NZD | -0.54% | -0.12% | -0.31% | -0.08% | -0.43% | -0.11% | -0.18% | |
| CHF | -0.38% | 0.05% | -0.13% | 0.07% | -0.24% | 0.04% | 0.18% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/USD (quote).
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD struggles to break above 1.0950
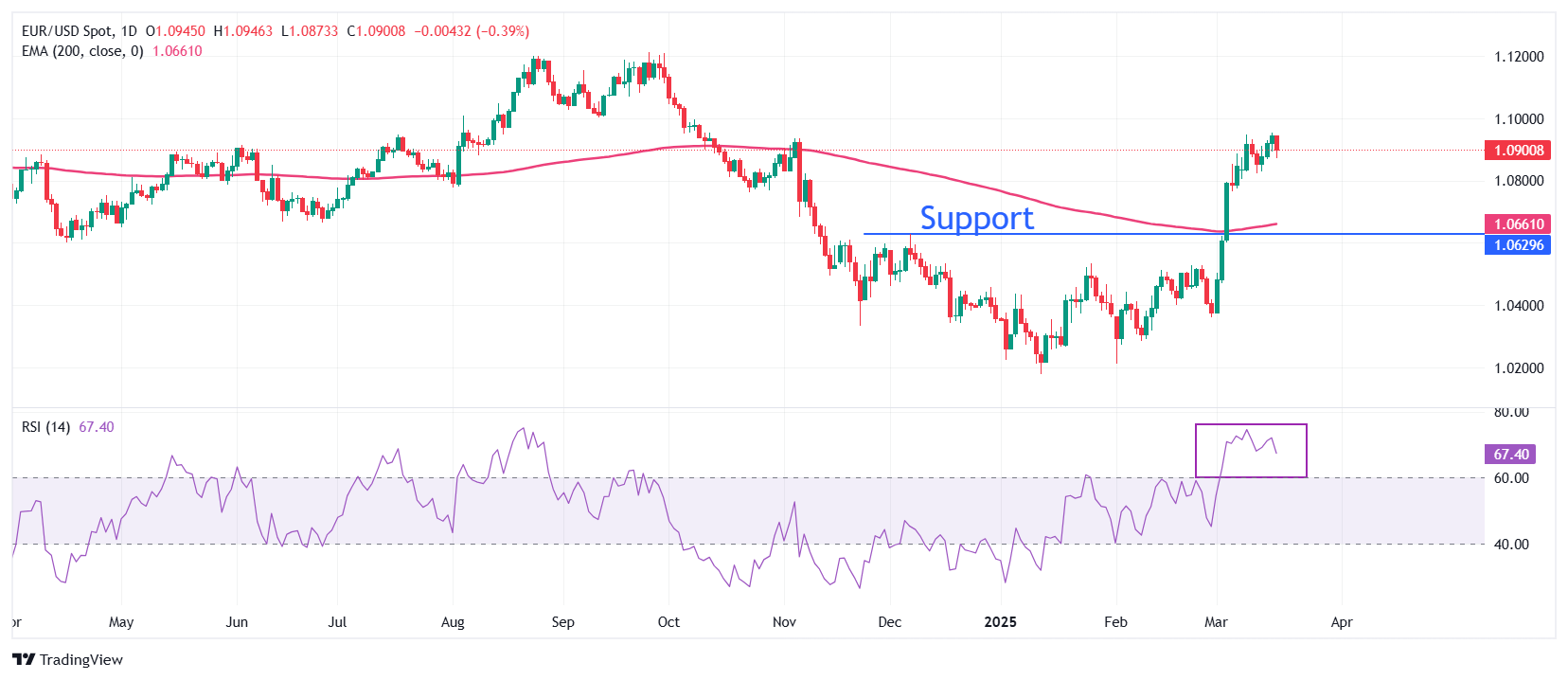
EUR/USD struggles to extend its upside above 1.0950. However, the long-term outlook of the major currency pair remains firm as it holds above the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.0660.
The pair strengthened after a decisive breakout above the December 6 high of 1.0630 on March 5.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) wobbles near 70.00, suggesting that a strong bullish momentum is intact.
Looking down, the December 6 high of 1.0630 will act as the major support zone for the pair. Conversely, the psychological level of 1.1000 will be the key barrier for the Euro bulls.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.





















