US Dollar unmoved with traders consolidating the Greenback at current levels
- The US Dollar remains flat after US opening bell on Thursday.
- US Retail Sales came in very mixed while weekly Jobless Claims got tainted by the Los Angeles wild fires.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) floats around 109.00 and does not seem to break away in any direction.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, is consolidating further this Thursday around 109.00 on Thursday after US Retail Sales and weekly Jobless Claims got released. The data distorted a clear sense of direction for the DXY with upside revisions in Retail Sales while the actual number was below expectations. The Los Angeles wild fires meanwhile is pushing the Jobless Claims higher.
Next up as final data point for this Thursday is the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) Housing Market Index for January. Nothing market moving expected there. Though the elevated rate regime could impact sentiment in the housing market in a negative way.
Daily digest market movers: There is the turn
- The US Retail Sales and the weekly Jobless Claims were released:
- The monthly Retail Sales fell to only 0.4%, lower than the 0.6% expected for December, compared to 0.7% the previous month. That same 0.7% got revised up to 0.8%.
- Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending January 10 came in higher to 217,000, while the previous 201,000 got revised to 203,000.
- The Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Survey for January came in at 44.3, beating the -5. The previous -16.4 got revised up as well -10.9.
- At 15:00, the NAHB Housing Market Index for January will be released. The expectation is that it will tick down to 45, compared to 46 in the previous reading.
- Equities are now down for this Thursday. Traders are starting to book profit on disinflation-infused positions from Wednesday.
- The CME FedWatch Tool projects a 97.3% chance that interest rates will be kept unchanged at current levels in the January meeting. Expectations are for the Federal Reserve (Fed) to remain data-dependent with uncertainties that could influence the inflation path once President-elect Donald Trump takes office on January 20.
- The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.653%, over 2.5% lower than its peak performance this week on Tuesday at 4.807%.
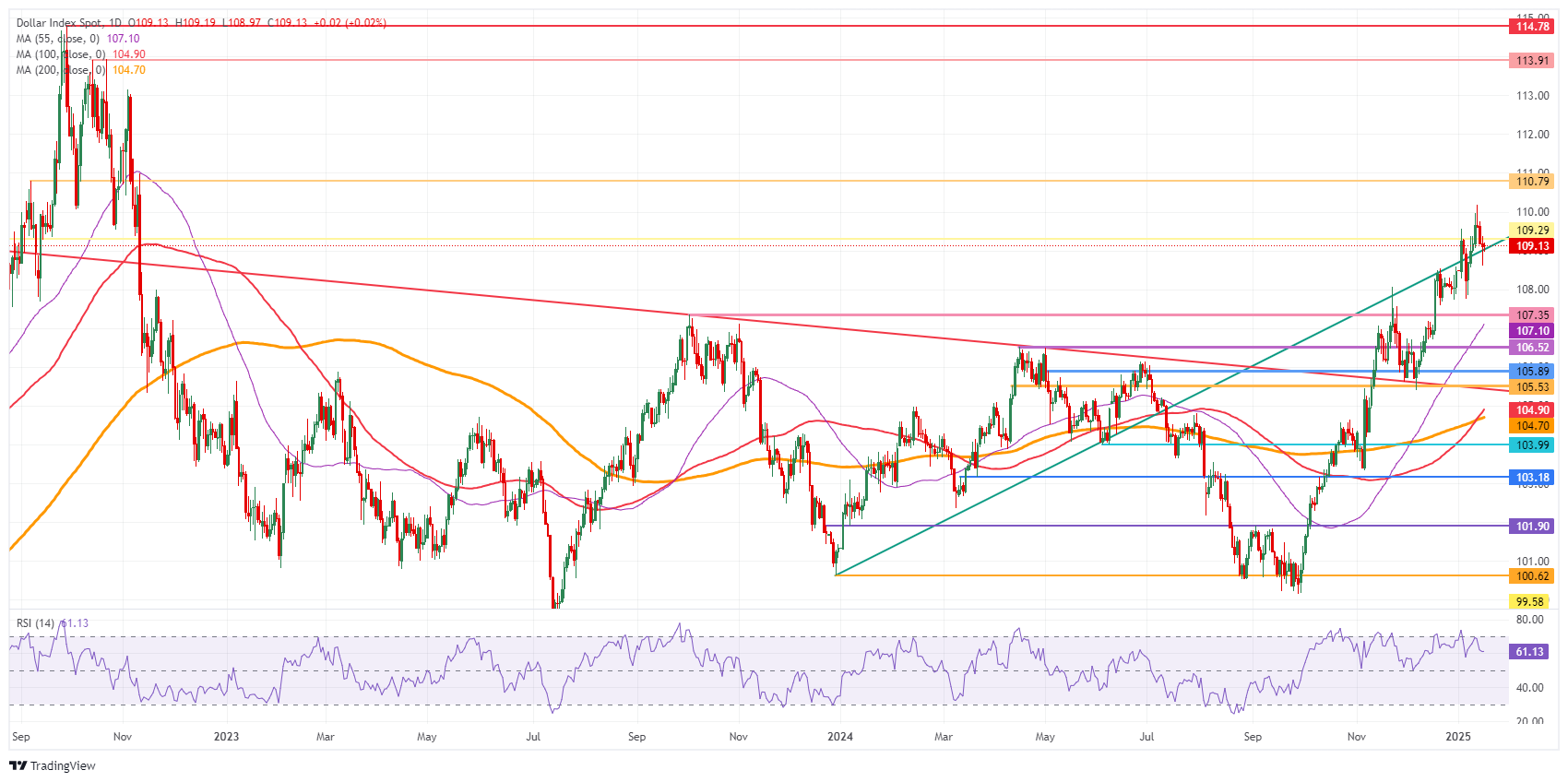
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Scrambled eggs
The US Dollar Index (DXY) takes a step back and is either on the verge of salvaging this rally or at risk of a harsh correction. Although markets might be rejoicing, mixed inflation data perceived as disinflationary will not have the Federal Reserve committing to anything at any time. Inflation might still elope and start turning hot and higher again, which would mean much more upside for the DXY, with markets being currently wrong-footed based on just one ‘mild’ disinflationary report at the start of the year.
On the upside, the 110.00 psychological level remains the key resistance to beat. Further up, the next big upside level to hit before advancing any further remains at 110.79. Once beyond there, it is quite a stretch to 113.91, the double top from October 2022.
On the downside, the DXY is testing the ascending trend line from December 2023, which currently comes in around 108.95 as nearby support. In case of more downside, the next support is 107.35. Further down, the next level that might halt any selling pressure is 106.52, with interim support at the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 107.10.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Interest rates FAQs
Interest rates are charged by financial institutions on loans to borrowers and are paid as interest to savers and depositors. They are influenced by base lending rates, which are set by central banks in response to changes in the economy. Central banks normally have a mandate to ensure price stability, which in most cases means targeting a core inflation rate of around 2%. If inflation falls below target the central bank may cut base lending rates, with a view to stimulating lending and boosting the economy. If inflation rises substantially above 2% it normally results in the central bank raising base lending rates in an attempt to lower inflation.
Higher interest rates generally help strengthen a country’s currency as they make it a more attractive place for global investors to park their money.
Higher interest rates overall weigh on the price of Gold because they increase the opportunity cost of holding Gold instead of investing in an interest-bearing asset or placing cash in the bank. If interest rates are high that usually pushes up the price of the US Dollar (USD), and since Gold is priced in Dollars, this has the effect of lowering the price of Gold.
The Fed funds rate is the overnight rate at which US banks lend to each other. It is the oft-quoted headline rate set by the Federal Reserve at its FOMC meetings. It is set as a range, for example 4.75%-5.00%, though the upper limit (in that case 5.00%) is the quoted figure. Market expectations for future Fed funds rate are tracked by the CME FedWatch tool, which shapes how many financial markets behave in anticipation of future Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.